In recent years molded pulp packaging has earned significant attention as companies look for packaging that aligns with environmental goals and regulatory changes. Many buyers appreciate that it turns discarded paper into a functional material that can cushion fragile items, support food service operations, and present products in a clean and natural way. Its ability to be recycled or composted after use also places it in a favorable position among modern sus
As demand continues to grow, more businesses are asking how molded pulp packaging works and how it compares with traditional plastic options. This article explores the production process, the fiber materials involved, the common types used today, and the advantages it offers in real operations. By understanding these elements, packaging buyers can make informed decisions that support both performance and sustainability goals.
How Is Molded Pulp Packaging Made
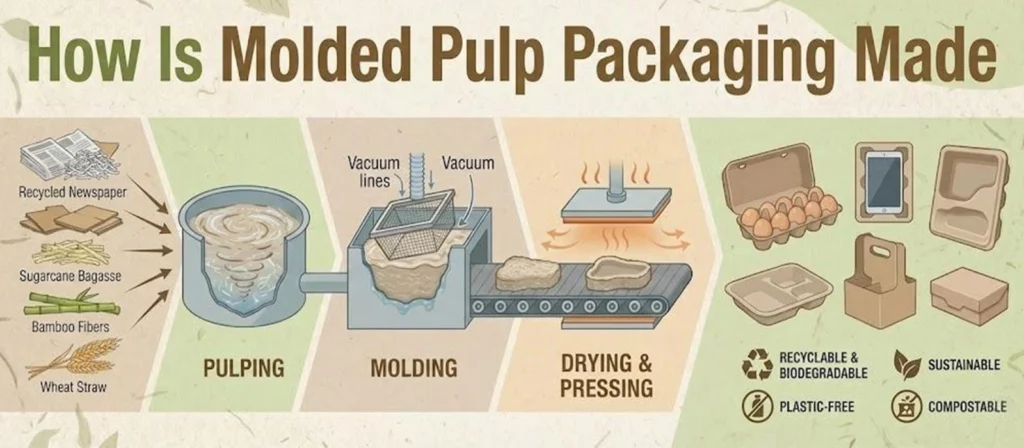
Molded pulp packaging is created through a structured production process that transforms recycled fibers into strong and reliable packaging forms. Each stage has a clear purpose and directly influences the final strength, surface quality, and consistency of the molded pulp packaging. Understanding this workflow helps buyers evaluate not only the material but also the manufacturing capability behind it.
- Pulping: Recycled paper is mixed with water and refined into a smooth fiber slurry. This step ensures that the fibers separate properly and can form an even structure once they enter the mold.
- Forming: The pulp slurry is drawn onto a mesh mold with controlled suction. Water drains away while fibers interlock on the mold surface, creating the initial shape that will later become the tray, insert, or protective shell.
- Pressing: The wet piece is transferred to a heated press where pressure and controlled heat remove additional moisture. This stage improves rigidity, enhances dimensional accuracy, and ensures the packaging can support products securely.
- Drying: The semi formed piece moves into a drying system to eliminate remaining moisture. Proper drying is essential for achieving stable strength, preventing deformation, and preparing the packaging for later handling.
- Finishing: The dried part is trimmed and refined to achieve clean edges and a uniform appearance. Some products may receive optional surface improvements so they can meet branding, hygiene, or automation requirements.
These steps work together to produce molded pulp packaging that is dependable, consistent, and suitable for modern commercial use. The process remains resource efficient while still delivering strong protective performance.
What Materials Are Used to Make Molded Pulp Packaging
Molded pulp packaging relies on fiber sources that balance performance, sustainability, and availability. Each material contributes different qualities that affect strength, surface finish, and suitability for food contact. The following sections introduce the most common materials used in molded pulp packaging and how they support food service and other industries.
1. Recycled Paper Pulp
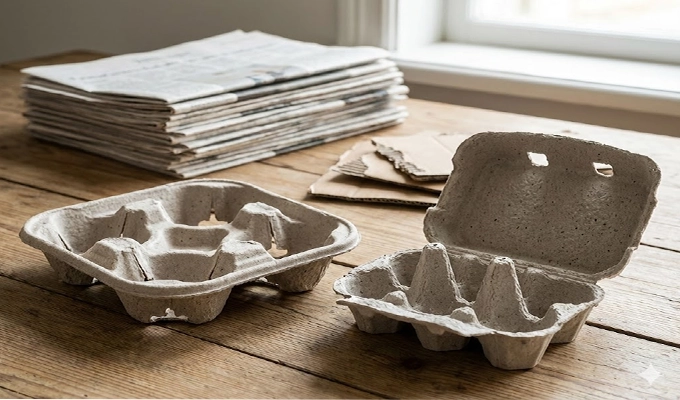

Recycled paper pulp remains the primary material for molded pulp packaging due to its wide availability and balanced performance. It is sourced from newspapers, office paper, cardboard offcuts, and other recovered fibers that can be efficiently reprocessed. This makes it one of the most cost effective and environmentally responsible choices for large scale food packaging production.
- Material Characteristics: Offers reliable rigidity, stable bonding between fibers, and good mold adaptability for common shapes.
- Application Scenarios: Widely used in cup carriers, snack trays, egg cartons, and general purpose food inserts.
2. Cardboard Pulp
Cardboard pulp comes from corrugated boxes and paperboard waste with longer and stronger fibers. These fibers create molded pulp packaging with enhanced compression resistance and greater durability, allowing for deeper or heavier packaging formats. It is often selected when the packaging must maintain shape under weight or stacking pressure.
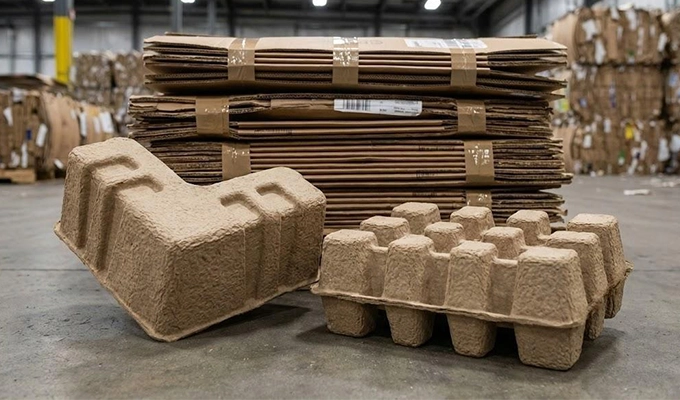

- Material Characteristics: Provides strong sidewalls, improved load bearing performance, and better resistance to crushing.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for produce trays, multi portion food containers, bakery transport trays, and industrial protective packaging.
3. Bagasse Fiber
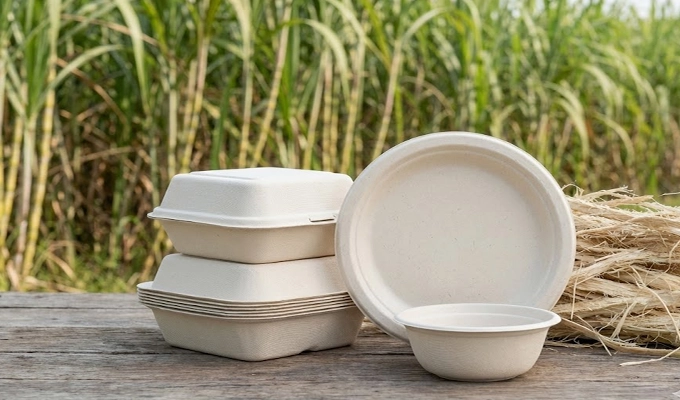

Bagasse fiber is a natural byproduct from sugarcane production. After extraction, the remaining fibers are cleaned and refined into pulp, creating a food safe material commonly used in restaurants and takeaway services. Its natural heat resistance and smooth finish allow molded pulp packaging made from bagasse to replace many traditional single use plastic items.
- Material Characteristics: Withstands high temperature foods, maintains structure with sauces or oils, and supports commercial composting.
- Application Scenarios: Common in bowls, plates, compartment trays, and takeaway meal boxes.
4. Bamboo Fiber
Bamboo fiber is derived from fast growing bamboo plants and is valued for its strength and refined appearance. The fibers are naturally long, which produces molded pulp packaging with excellent surface quality and enhanced durability. It is often chosen by brands that need packaging to look premium without compromising environmental responsibility.
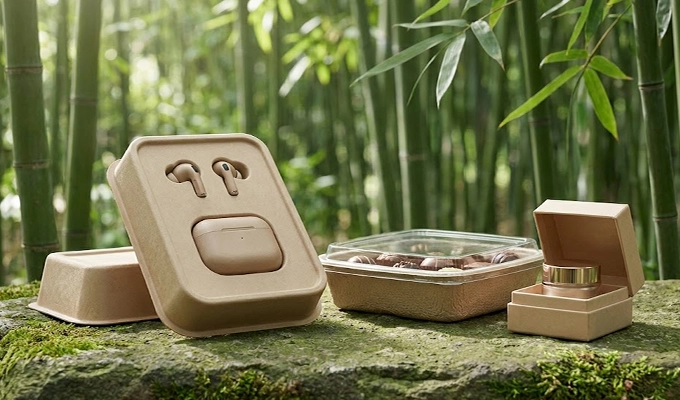

- Material Characteristics: Delivers a smooth natural finish, strong fiber bonding, and a clean aesthetic suitable for premium goods.
- Application Scenarios: Used in upscale food packaging, luxury snack trays, and specialty molded inserts.
5. Wood Pulp
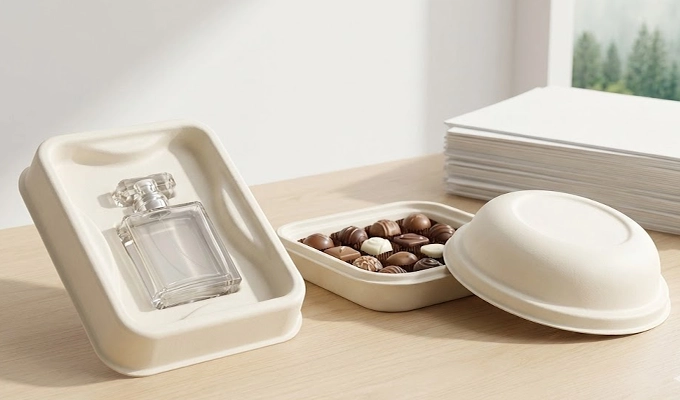

Wood pulp uses virgin fibers from responsibly managed forests and is known for its purity and consistency. It produces molded pulp packaging with precise detail and uniform color, which is important for packaging that must meet strict food safety or product presentation requirements. The fibers are refined to ensure excellent moldability and stability.
- Application Scenarios: Found in food service lids, premium trays, protective inserts for delicate foods, and specialized packaging.
- Material Characteristics: Ensures high performance in fine detailing, predictable texture, and strong structural reliability.
Summary Table of Materials Used in Molded Pulp Packaging
| Material | Key Characteristics | Typical Food Packaging Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Recycled Paper Pulp | Reliable strength and balanced cost | Cup carriers, food trays, snack inserts |
| Cardboard Pulp | Strong fiber structure and high compression resistance | Produce trays, heavier food containers |
| Bagasse Fiber | Heat tolerant and suitable for oily foods | Plates, bowls, takeaway meal boxes |
| Bamboo Fiber | Premium appearance and durable fibers | High end trays and specialty food packaging |
| Wood Pulp | Pure fiber quality and detailed molding capability | Lids, premium trays, delicate food inserts |
What Types of Molded Pulp Packaging Are Common Today
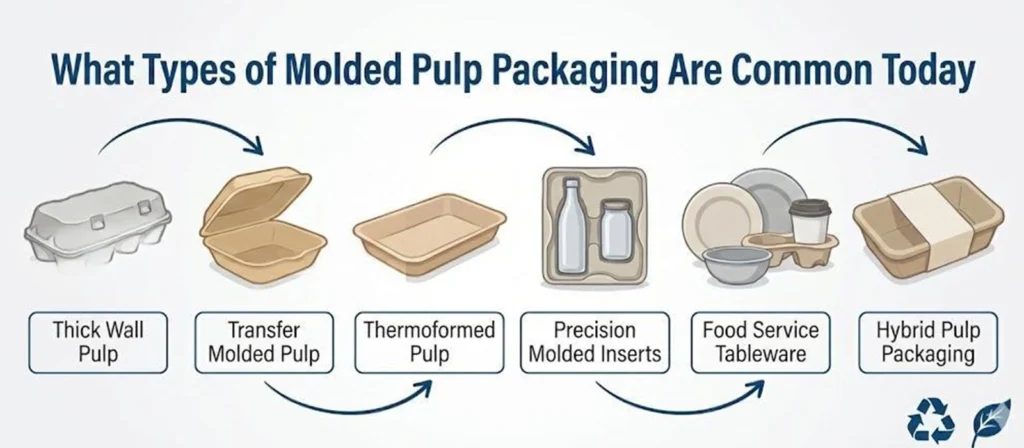
Molded pulp packaging has expanded far beyond basic trays and cup carriers, and different forming methods now create packaging that fits a wide range of food service needs. Each type offers its own level of detail, strength, and production cost, which affects how brands use molded pulp packaging in real operations.
Traditional Thick Wall Pulp Packaging
This type is made with a lower vacuum level and thicker fiber layers, resulting in a sturdy structure. The surfaces are slightly rougher, but the strength allows it to support fresh produce, food portions, and general protective use. It is commonly chosen for items that do not require a premium appearance yet still need dependable cushioning.
Transfer Molded Pulp Packaging
This process forms the pulp on one mold and transfers it to another for improved shaping. The result is a cleaner surface, more accurate contours, and a lighter overall weight. Food service businesses use this type for takeaway trays, food clamshells, and bowl bases because it balances appearance and strength.
Thermoformed Pulp Packaging
Thermoformed pulp goes through heated molds that compress the fibers more thoroughly, creating a smooth, refined finish. This type is often used when packaging must look premium, stack neatly, or fit into automated packing lines. High end bakery trays, dessert containers, and branded food inserts rely on this method.
Precision Molded Inserts
These inserts are engineered to fit specific product shapes with tight tolerances. While commonly used for electronics, cosmetics, or glass items, they also serve food categories such as gift snack sets and delicate confectionery. Their strength and shape accuracy allow products to stay secure without excess wrapping.
Food Service Tableware
Many molded pulp items are created specifically for direct food contact, including plates, bowls, compartment trays, cup carriers, and hot food containers. These products perform well with both hot and cold meals, and materials like bagasse or bamboo fiber enhance heat tolerance.
Hybrid Pulp Packaging
This type combines molded pulp with outer wraps, labels, or coatings to achieve specific functions such as moisture resistance or enhanced presentation. Some food brands use hybrid formats to elevate shelf appeal while keeping the main structure fiber based.
Key Points of Each Production Method
- Thick Wall Pulp: Focuses on strong fiber layers and impact absorption, suitable for produce and heavier food items.
- Transfer Molded Pulp: Delivers a cleaner surface and lighter weight, commonly used for takeaway trays and clamshells.
- Thermoformed Pulp: Provides the smoothest finish and best molding accuracy, ideal for premium food packaging.
- Precision Molded Inserts: Designed for tight fitting protection and stable positioning of delicate goods.
- Food Service Tableware: Created for direct food contact with heat tolerance and everyday practicality.
- Hybrid Pulp: Combines molded pulp structure with functional finishes for better appearance or moisture resistance.
These common types allow molded pulp packaging to support grocery produce, restaurant takeaway, bakery items, online retail, and premium food gifting. The variety also ensures businesses can match performance needs with appropriate production methods.
Molded Pulp Packaging vs Plastic Packaging
Molded pulp packaging and plastic packaging are both widely used across food service, retail, and transportation. Although they serve similar purposes, the two materials differ in environmental performance, production methods, and suitability for specific applications.
Comparison Table: Molded Pulp Packaging vs Plastic Packaging
| Aspect | Molded Pulp Packaging | Plastic Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Made from recycled paper, bagasse, bamboo fiber, or wood pulp that comes from renewable or reclaimed resources | Made from petroleum based polymers that rely on non renewable fossil fuels |
| Environmental Impact | Naturally biodegradable and often compostable, contributing less long term waste | Long decomposition cycles and often difficult to recycle due to mixed polymer types |
| Food Safety Performance | Handles hot and cold foods with stable structure and minimal chemical concerns | Performs well with liquids and high moisture foods but may involve additives that raise safety questions |
| Strength and Durability | Provides strong cushioning and good rigidity for many food items and lightweight goods | Offers high flexibility, water resistance, and impact tolerance especially for liquids |
| Surface Appearance | Natural matte finish suitable for eco friendly branding and minimalist design | Smooth glossy finish suitable for high visibility retail display |
| Customization Capability | Supports molded shapes, embossing, and cavity design with moderate detail | Offers very high detail, transparency, and tight dimensional precision |
| Cost Structure | Competitive for medium to high volume production when fiber resources are available | Cost effective for mass production once molds and tooling are established |
| End of Life Pathways | Recyclable in paper streams and often accepted in composting facilities | Mostly landfilled unless local recycling programs accept the specific resin type |
| Regulatory Compliance | Increasingly aligned with global regulations favoring fiber based packaging | Facing rising restrictions as many regions move away from single use plastics |
Molded pulp packaging and plastic packaging each hold advantages depending on product type, required performance, and disposal expectations. By comparing their core characteristics, businesses can select the solution that supports both operational efficiency and sustainability targets。
How Can Businesses Choose the Right Molded Pulp Packaging

Selecting molded pulp packaging must focus on real performance needs rather than general impressions. The points below help businesses evaluate materials, structure, and cost so the final choice supports both product protection and operational efficiency.
- Product Weight and Structure Needs Heavy or multi portion foods require thicker walls, stronger fibers, and tighter bonding. Lighter bakery items or produce often work well with transfer molded or thermoformed pulp.
- Shape and Fit Accuracy Products with multiple components or fragile edges benefit from precision molded cavities. Simple shapes can use standard trays to lower costs and reduce tooling time.
- Material Selection for Food Contact Bagasse works well for hot foods and oily meals. Bamboo and wood pulp offer cleaner surfaces for items requiring a premium appearance. Recycled fiber suits general takeaway containers.
- Moisture and Heat Performance Hot foods above roughly 80 degrees Celsius need heat tolerant fibers such as bagasse. Items with high moisture content require stronger pressing or smoother thermoformed surfaces for stability.
- Customization Requirements Custom molds improve fit and reduce movement, especially for retail food sets. Thermoformed pulp provides better branding options through cleaner lines and refined surfaces.
- Budget and Volume Planning Recycled paper and mixed fiber blends deliver cost efficiency for medium and large volume orders. Premium fibers like bamboo increase unit cost but improve presentation. High volume orders lower tooling impact.
- Regulatory Compliance Food contact packaging must meet standards such as FDA or EU migration limits. Virgin wood pulp provides more consistent test results when compliance is strict.
- Sustainability Expectations Businesses aiming for compostable or recyclable packaging should prioritize bagasse or recycled fibers. Blended fibers may require verification depending on disposal conditions.
- Storage and Transport Conditions Long distance delivery or stacked storage requires higher compression strength. Transfer molded or thick wall pulp performs better under stacking pressure.
Choosing the right molded pulp packaging becomes much easier when decisions are based on real product needs, financial planning, and regulatory expectations. Evaluating samples and testing them under normal use conditions ensures reliable performance and reduces long term risk.
What Is the Future Outlook for Molded Pulp Packaging
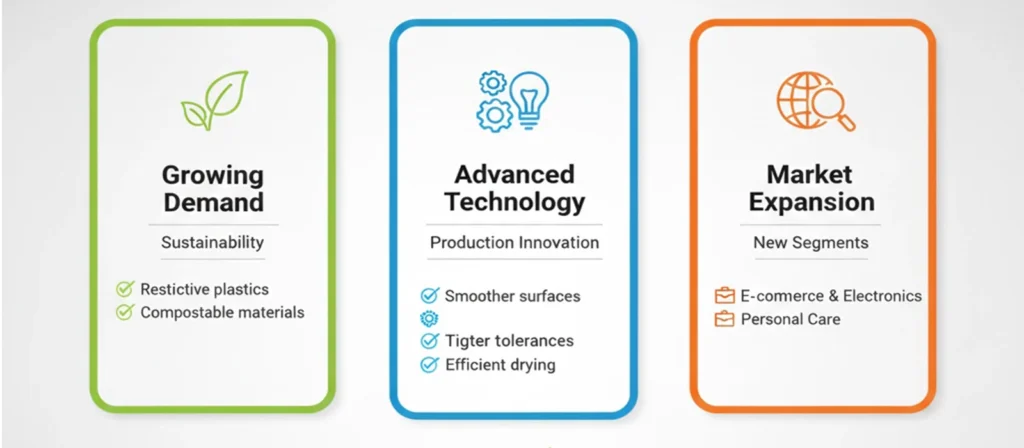
The future of molded pulp packaging is shaped by sustainability demands, material innovation, and global policy changes. Although the industry is already expanding, several trends indicate even stronger growth in the coming years.
1. Growing Demand Driven by Sustainability
More regions are restricting single use plastics, and businesses are actively seeking fiber based alternatives. Molded pulp packaging is expected to grow steadily as companies prioritize recyclable and compostable materials that reduce long term waste.
2. Advances in Material and Production Technology
Improved forming systems, better drying efficiency, and refined fiber blends will allow molded pulp packaging to achieve smoother surfaces, tighter tolerances, and higher durability. These upgrades support food service, retail, and premium product categories that require cleaner design and consistent performance.
3. Expansion into New Market Segments
Beyond food service, molded pulp packaging is expected to increase its presence in personal care, electronics, and e commerce protective packaging. More brands will adopt molded pulp solutions as they adapt to environmental regulations and seek stronger sustainability credentials.
The combined force of policy changes, technological progress, and consumer expectations positions molded pulp packaging as one of the most reliable long term materials for modern packaging。
Conclusion
Molded pulp packaging offers a practical balance of performance, sustainability, and versatility for modern food service and retail operations. By understanding its materials, production methods, and application possibilities, businesses can choose solutions that support product protection while meeting environmental and regulatory expectations. As technology advances and global demand shifts toward renewable materials, molded pulp packaging is positioned to become an increasingly important part of the packaging landscape.







