Die cutting is a precision manufacturing process that uses a specialized tool called a die to cut, shape, or form materials into specific designs. In the packaging industry, it is widely used to create consistent, repeatable shapes such as boxes, labels, inserts, cartons, and custom components. By applying pressure through a die onto materials like paperboard, cardboard, corrugated board, or plastic films, manufacturers can produce highly accurate cuts at high speed and large scale.
At its core, die cutting functions like an industrial version of cookie-cutting: a pre-designed metal die stamps out the required shape, ensuring every piece is identical. This accuracy and repeatability make die cutting a critical step in modern packaging production, especially for brands that require strong visual consistency and structural reliability.
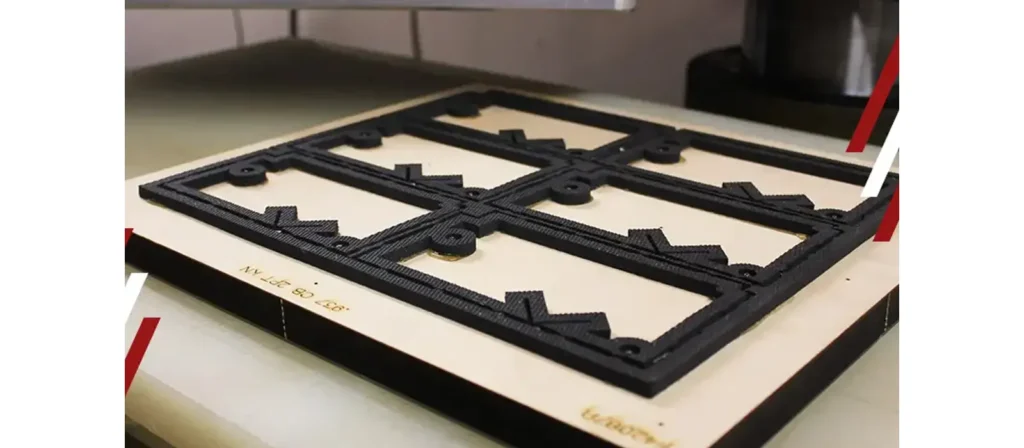

Types of Die Cutting Techniques
Die cutting techniques vary based on production speed, material type, and the level of detail required in the final design. Each method offers unique strengths, allowing manufacturers to choose the most efficient approach for boxes, labels, inserts, and other packaging components. Understanding these different techniques helps determine the right balance between precision, cost, and scalability.
1. Flatbed Die Cutting
Flatbed die cutting uses a flat die and vertical pressure to create clean, accurate cuts. It is ideal for thicker substrates such as corrugated board and offers excellent precision for structural packaging.
2. Rotary Die Cutting
Rotary die cutting uses a rotating cylindrical die, making it highly efficient for continuous, high-volume production. It delivers consistent results at fast speeds and is commonly used for labels, films, and folding cartons.
3. Digital or Laser Die Cutting
Digital cutting eliminates the need for a physical die, using a laser or blade to cut directly from a digital design. It is best suited for short runs, rapid prototyping, and intricate shapes where flexibility is more important than speed.
How Die Cutting Works
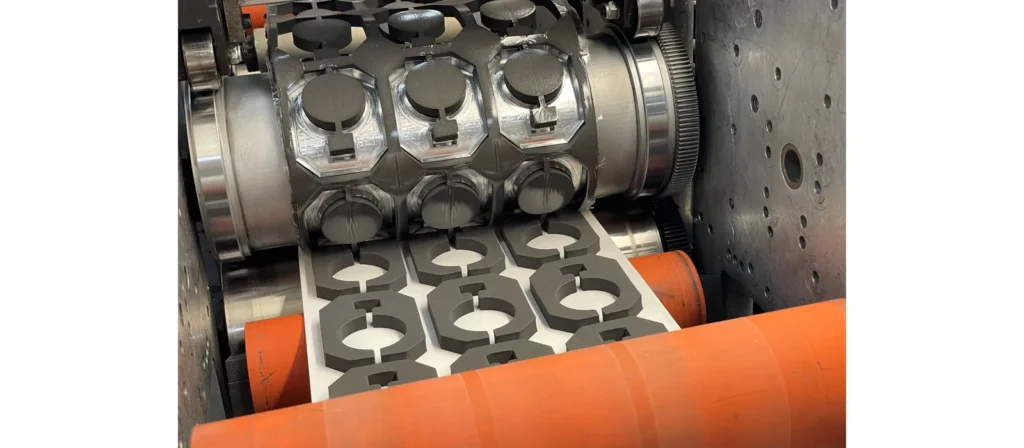
Die cutting works by using a custom-built metal tool called a die to cut or shape a material into a specific design needed for packaging. The process begins with engineers creating a structural layout that defines every element of the package, including cut lines, crease lines, perforations, and tabs. Based on this layout, a die is manufactured and mounted inside a die-cutting machine.
During production, sheets or continuous rolls of material are fed into the machine. As they pass through, the die applies precisely controlled pressure to the material, cutting or creasing it exactly as designed. When the shapes have been formed, the excess material is removed, leaving only the finished components ready for folding, gluing, or assembling into final packaging structures.
The Die-Cutting Process in Packaging
Dieline
The die-cutting process begins with designing the dieline, which acts as the structural blueprint for the entire package. It outlines every cut, crease, tab, fold, and locking system. Engineers assess material thickness, required volume capacity, machine compatibility, assembly direction, and nesting efficiency. A well-developed dieline ensures structural stability, clean folding behavior, efficient material usage, and consistent performance during mass production. Any imperfections at this stage can lead to misalignment, weak corners, or assembly difficulties later in the process.
Select the Right Die-Cut Method
Once the dieline is completed, the next step is selecting the appropriate die-cutting method based on the structural complexity and functional requirements of the packaging. Each method delivers different outcomes and is suitable for specific use cases. Choosing the right one ensures cut accuracy, shape consistency, and optimal functionality.
| Method | How it works |
|---|---|
| Blanking | Full cut through sheet |
| Drawing | Pulls material into 3D cavities |
| Forming | Bends material into shape |
| Coining | Compresses material for detail |
| Broaching | Removes internal patterns |
Engineers select one or combine several of these methods depending on the packaging’s purpose, complexity, and required visual or functional features.
Choose the Cut Styles for Functionality
After selecting the die-cutting method, the next step is choosing the appropriate cut styles that determine how the packaging behaves during folding, filling, opening, and consumer use. Each cut style serves a specific purpose and contributes to structural performance, user convenience, or branding value. The following options are commonly used in die-cut food packaging and general paperboard applications:
| Cut Style | How it Works |
|---|---|
| Kiss Cut | Cuts only the top layer of material while leaving the backing intact |
| Through Cut | Cuts completely through the material |
| Perforation | Creates a dotted cut line for controlled tearing |
| Creasing / Scoring | Compresses fibers to form fold lines without cracking |
| Embossing / Debossing | Raises or recesses the surface to create tactile detail |
Choosing the right combination of these cut styles ensures that the packaging functions as intended. Clean folds, secure closures, smooth edges, vent openings, and branded textures all contribute to better usability and product protection. By tailoring cut styles to the food type, assembly workflow, and customer experience, manufacturers can achieve packaging that performs reliably while enhancing visual impact.
Build the Die & Ensure Cutting Precision
After the cut styles and methods are finalized, the tooling team constructs the die. Steel rule blades are shaped and inserted into the die board with highly controlled tolerances. Creasing channels, rubber ejectors, and alignment markers are added to ensure optimal pressure, clean edges, consistent crease depth, and long-run stability. The die is tested and refined until every detail matches the dieline precisely. Accurate die construction prevents defects such as uneven cuts, fiber tearing, weak folds, and poorly aligned locking systems.
Die Cutting Execution & Quality Control
In the production phase, sheets or continuous rolls of material are fed into the machine and cut according to the die. Operators fine-tune pressure, feeding alignment, and speed to match the material characteristics and structural requirements. Quality control teams conduct ongoing inspections to verify edge cleanliness, crease accuracy, dimensional consistency, locking performance, and overall structural integrity. Samples are folded and tested to ensure that closures engage properly, trays hold their shape, and no tearing or cracking occurs. Effective monitoring ensures stable output, reliable assembly, and consistent performance across all units.
Applications of Die Cutting in Packaging
Die cutting is used across a wide range of packaging industries because it allows manufacturers to produce accurate, repeatable shapes from paperboard, cardboard, and similar substrates. Its flexibility makes it suitable for both structural components and decorative elements, supporting applications in food service, retail, consumer goods, and promotional packaging. No matter the industry, die cutting helps ensure clean edges, precise folds, and consistent results from one unit to the next.
In the food packaging sector, die cutting plays a central role in forming a variety of containers and service-ready packaging. Products such as round-bottomed bowls, square takeout buckets, salad boxes, sandwich boxes, and hamburger boxes all rely on precisely cut layouts that fold cleanly into their final shapes. The same technology is essential for producing pizza boxes, cake boxes, lock-bottom boxes, hexagonal boxes, and other structural designs that must securely hold and protect food items. Inner trays, liners, boat-shaped food trays, snack scoops, and box lids also depend on die-cut precision for easy assembly and reliable performance.

Beyond food service, die cutting is used to manufacture retail packaging, display cards, custom sleeves, gift boxes, and branding elements such as tags and inserts. Industries such as cosmetics, electronics, and apparel commonly use die-cut components to enhance presentation or support product protection. Even items like wrapping paper sheets, promotional mailers, and shaped retail displays benefit from die cutting’s ability to produce consistent forms at large scale.
Typical die-cut packaging products include:
- Round-bottomed bowls and rectangular/square bowls
- Square takeout buckets and glued square food boxes
- Salad boxes, sandwich boxes, and hamburger boxes
- Pizza boxes and cake boxes
- Lock-bottom, hexagonal, and square-corner food boxes
- Inner trays, liners, and boat-shaped food trays
- Snack cups, boxes, and scoops
- Box lids, outer layers, and lidless box bases
- Retail display cards, tags, sleeves, and insert cards
- Wrapping paper and promotional die-cut sheets
This range of applications demonstrates how die cutting supports both functional performance and brand presentation across multiple industries, while remaining a cornerstone of modern paper-based packaging.
Need Custom Food Packaging?
Looking for tailor-made food packaging that fits your brand and product needs? Million Pack provides professional customization services for paper bowls, boxes, trays, and more. Share your requirements and let us help you create packaging that truly stands out.
 Start Your Custom Project
Start Your Custom Project
What to Consider for Die-Cut Food Packaging?
Designing die-cut food packaging requires careful evaluation of material safety, structural performance, usability, and cost efficiency. To ensure the packaging functions well across different food types and service environments, consider the following key factors:
- Material Safety
Use food-grade paperboard or coated materials that meet hygiene and regulatory standards. - Grease and Moisture Resistance
Consider coatings or laminations to prevent leakage, softening, or oil absorption. - Structural Strength
Ensure the paper weight, crease accuracy, and locking features support the food’s weight and shape. - Ease of Assembly
Designs should fold smoothly and allow quick assembly for fast-paced foodservice environments. - Temperature Compatibility
Choose materials suitable for hot meals, cold foods, or both, depending on the application. - Brand Presentation
Die-cut windows, shapes, and clean edges help improve the packaging’s visual appeal. - Cost and Production Efficiency
Optimized die layouts reduce waste and help maintain cost-effective mass production.
By balancing safety, durability, usability, branding, and production efficiency, manufacturers can create die-cut food packaging that performs reliably while supporting both customer needs and business goals.
The Critical Role of Die Cutting in the Packaging Industry
Ensuring Precision and Structural Reliability
Die cutting plays a vital role in delivering the accuracy needed for high performance packaging. By placing every cut line and fold line in the exact intended position, it ensures that packaging structures assemble smoothly and maintain their shape during use. Food boxes, trays, retail sleeves, and specialty cartons depend on this precision to function properly and protect the products inside.
Supporting Scalable and Stable Mass Production
A key function of die cutting is its ability to maintain quality across large production volumes. Packaging for takeaway food, bakery items, cosmetics, and consumer goods requires consistent output at high speed. Die cutting supports this need by producing thousands of pieces per hour while keeping the shape, size, and performance of each unit stable.
Enabling Diverse and Innovative Packaging Designs
The packaging industry depends on die cutting to create the wide variety of shapes and structures required by different brands. From simple cartons to complex folding designs, die cutting enables windows, openings, locking mechanisms, and creative silhouettes. These design possibilities make it easier for brands to stand out and enhance customer experience.
Integrating Functional Finishing Features
Die cutting works hand in hand with finishing techniques that improve the practicality of packaging. Scoring helps cartons fold cleanly, perforating enables easy tearing, and embossing adds texture or visual interest. These features contribute to a better final product and support more efficient assembly during manufacturing.
Improving Material Efficiency and Sustainability
Efficient material use is essential in modern packaging production. Die cutting layouts are carefully planned to maximize yield and reduce waste, making the process both economical and environmentally responsible. By helping manufacturers use fewer resources, die cutting supports sustainability goals across the industry.
Partner With Million Pack for Custom Die Cut Packaging
If you are looking for reliable, high quality die cut packaging that aligns with your brand and product needs, Million Pack is ready to support you. With deep experience in producing food grade paper bowls, boxes, trays, and custom structural designs, we offer professional guidance from concept to final production. Our team can help you select suitable materials, optimize structural strength, and ensure that every detail from cutting lines to folding performance meets your quality expectations.
Whether you need custom shapes for branded food packaging, tailored structural solutions for retail products, or efficient mass production support, we provide flexible manufacturing options and stable supply capacity. To begin your project or request a quote, contact Million Pack and let our team assist you in creating packaging that is both practical and visually distinctive.







