Before such coatings became common, many food packages failed to control moisture, leaked easily, or lost strength when exposed to heat, oil, or freezer conditions. This led to product damage, hygiene concerns, and a poor consumer experience. After the introduction of well-designed Functional Coating for Food Packaging, manufacturers could create containers that hold boiling water, resist oil migration, survive frozen storage, and maintain clean surfaces throughout distribution.
This article serves as the bridge between problems and solutions. Just as a thoughtfully planned daycare floor plan turns chaotic rooms into efficient learning environments, understanding the principles behind Functional Coating for Food Packaging allows you to design packaging that is safer, more stable, more sustainable, and better suited for modern food demands. Through the lens of Extrusion Coating, you will see how the right material choices can elevate paper, board, and films into reliable, functional, and high-value food packaging systems.
Common Types of Functional Coating for Food Packaging
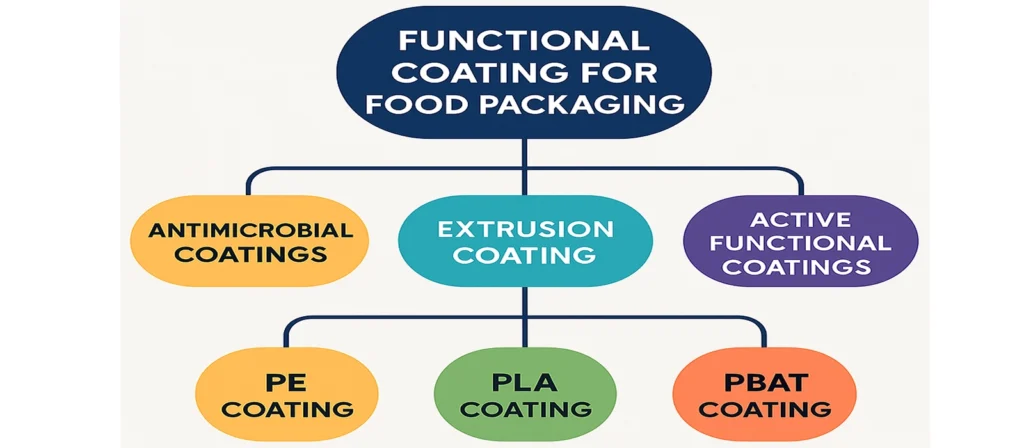
Below is a structured overview of major extrusion-coated materials used as Functional Coating for Food Packaging, written in list form as required and expanded where instructed.
Extrusion Coating:
1. PE Coating
- Single-layer PE
Function: Offers essential waterproof and grease-resistant performance, providing dependable protection when the package must endure hot water and steam contact.
Typical application: Used on instant noodle bowls to maintain structural stability during preparation and prevent leakage even under prolonged exposure to boiling conditions. - Double-layer PE
Function: Reduces condensation accumulation, enhances surface dryness, and maintains appearance when exposed to cold temperatures and fluctuating humidity levels.
Typical application: Commonly used on ice cream outer cartons to prevent moisture rings, surface stickiness, and weakening during extended freezer storage.
2. PLA Coating
- Single-layer PLA
Function: Provides a biodegradable and renewable moisture barrier suitable for applications seeking a balance between sustainability and practical performance.
Typical application: Applied to compostable salad bowls to deliver clean surface quality and protect against liquid absorption from vegetables and chilled foods. - Double-layer PLA
Function: Improves tolerance to oils and elevated temperatures, enabling broader use in bakery packaging where resistance to fat and heat is essential.
Typical application: Used on environmentally conscious baking papers for pastries, allowing easy food release and consistent quality during oven cycles.
3. PBAT Coating
- Single-layer PBAT
Function: Combines flexibility, water resistance, and biodegradability, providing enhanced fold durability and suitability for fast-moving food service formats.
Typical application: Utilized on grease-resistant sandwich wraps that must handle oily fillings while staying compatible with compostable waste systems. - Double-layer PBAT
Function: Supplies improved mechanical strength and moisture protection, delivering reliable performance for heavier foods and more demanding handling environments.
Typical application: Used on compostable takeaway boxes that transport hot, moist meals while maintaining form and resisting saturation.



Antimicrobial Coatings:
- Silver-ion structures that inhibit microbial activity and extend shelf integrity for fresh meat packaging, ensuring safer handling and improved product stability.
- Chitosan-based coatings that introduce natural antimicrobial effects for fruit and vegetable contact surfaces, helping maintain freshness throughout storage and transport.
Active Functional Coatings:
- Oxygen-scavenging layers designed to protect nuts, snacks, and other oxidation-sensitive products by reducing oxygen levels and preserving quality longer.
- Moisture-modulating coatings used to maintain the crisp texture of cookies and baked goods while balancing humidity variations during distribution and storage.
Comparison of PE, PLA, and PBAT in Extrusion-Coated Food Packaging
| Performance Factor | PE Coating | PLA Coating | PBAT Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Resistance | Strong moisture barrier suitable for hot water, boiling liquids, and frozen storage. Common in cups and instant bowls. | Moderate moisture barrier effective for chilled foods but less stable under high humidity or extended hot-water exposure. | Good moisture barrier with flexibility, performing well in wraps and takeaway formats exposed to steam or condensation. |
| Grease Resistance | Provides reliable grease resistance for oily foods and fast-food items, maintaining clean surfaces and preventing fiber weakening. | Offers controlled grease resistance suitable for bakery goods, pastries, and compostable salad formats that require clean presentation. | Excellent grease resistance ideal for sandwiches, hot meals, and foods with high oil content requiring compostable solutions. |
| Temperature Performance | Very good stability across both hot and cold applications, handling boiling water and deep-freeze cycles effectively. | Performs well under moderate heat and chilled conditions, but softens under high temperatures unless reinforced in double layers. | Good tolerance to warm and hot foods, maintaining flexibility at low temperatures and resisting cracking during handling. |
| Mechanical Strength | Provides notable stiffness and durability, protecting paper substrates in forming and filling operations. | Offers moderate strength, enhancing rigidity but requiring controlled processing to avoid cracking in high-stress applications. | High flexibility and toughness, increasing tear resistance and fold durability in compostable wraps and takeaway boxes. |
| Sustainability Profile | Fossil-based; recyclable in some controlled systems but less compatible with compostable streams. | Bio-based and industrially compostable, widely used in eco-focused packaging formats seeking renewable content. | Biodegradable with strong compatibility in compostable packaging systems, often paired with paper to reduce environmental impact. |
Applications of Extrusion Coating in Food Packaging
Modern packaging formats rely heavily on Extrusion Coating to achieve combinations of barrier performance, structural stability, and regulatory compliance. The following applications illustrate how different food categories benefit from tailored Functional Coating for Food Packaging strategies.
- Hot beverage cups and instant bowls rely on moisture-resistant inner layers that maintain stiffness and prevent leakage, especially when exposed to boiling water.
- Ice cream cartons need surfaces that resist condensation and retain structural strength at freezer temperatures, making double-layer PE ideal.
- Bakery totes, bags, and liners often use PLA or PBAT coatings to balance grease resistance, compostability, and printability.
- Takeaway cartons and clamshells depend on PBAT or hybrid coatings to manage oils, temperature variation, and high handling stress.
- Fresh produce packaging uses PLA coatings or active layers to regulate moisture, protect texture, and maintain visual appeal during chilled distribution.
Each represents a case in which the coating must be chosen specifically to match the food environment. By adjusting polymer type, coating thickness, and substrate selection, Extrusion Coating enables packaging designers to achieve both functional reliability and commercial practicality.



What is the manufacturing process of coating?
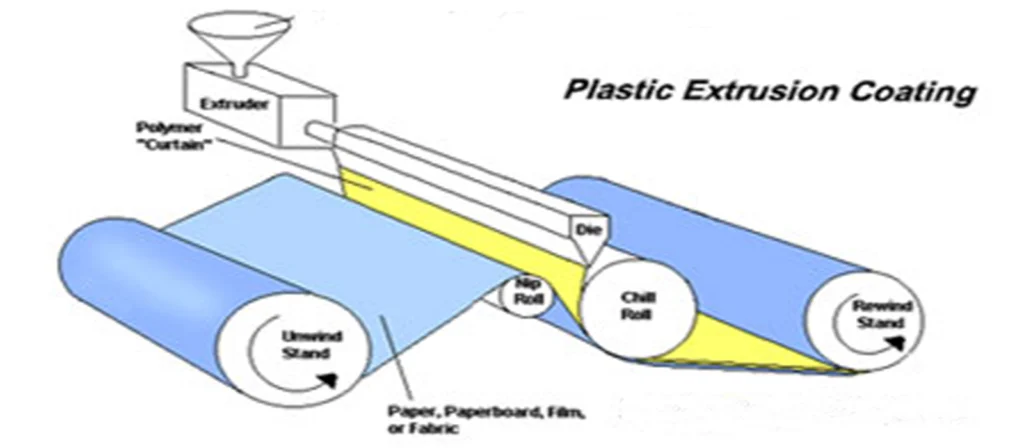
The Extrusion Coating process begins with polymer pellets fed into an extruder where they are melted, homogenized, and pushed through a flat die to form a continuous curtain of molten resin. This material is deposited onto a moving substrate positioned between the die and a chill roll. The combination of precise melt temperature, web speed, nip pressure, and cooling rate creates a thin, even layer that unites with the substrate surface. The result is a strong, uniform coating capable of serving as a moisture barrier, grease shield, or structural support layer.
Substrate adhesion plays a central role in determining final quality. Paper and film may require surface activation to raise surface energy, allowing the molten polymer to wet the substrate thoroughly. Chill roll temperature and nip pressure must be carefully controlled so the polymer solidifies at the right moment, ensuring consistent thickness and reliable bonding. These adjustments allow producers to create a coating optimized for the exact performance level required by the intended food category.
The method also supports extrusion lamination, in which the molten polymer bonds two substrates together. This expands the range of available structures and makes it possible to integrate barrier properties, print surfaces, or mechanical strength into one laminated format. For applications requiring multi-layer systems, tandem lines and co-extrusion techniques allow several resins to be applied simultaneously, improving barrier reliability without greatly increasing complexity.
The precision of Extrusion Coating is what makes it indispensable in delivering a high-quality Functional Coating for Food Packaging. Even a thin layer can drastically change a substrate’s properties, enabling designers to create lightweight, robust structures that meet the physical and regulatory challenges of food contact applications.
Challenges and Technical Considerations in Extrusion Coating

Several technical challenges influence the quality and stability of extrusion-coated structures, including:
- Printability and Surface Quality
Printing accuracy and visual consistency depend on well-managed surface properties. Manufacturers must maintain clean dies, effective surface treatment, and stable chill roll behavior to produce the high visual standards required for commercial food packaging. - Adhesion and Bonding
Adhesion between polymer and substrate must remain consistent, especially for bio-based materials with narrower processing windows. Poor bonding can lead to delamination, reduced barrier integrity, and failures during forming operations. - Curling and Dimensional Stability
Curling or distortion may occur when substrates expand or contract unevenly during coating. Proper tension control, balanced coating application, and moisture management help reduce these issues and support predictable converting performance. - Regulatory Compliance
All food-contact materials must meet safety standards, and additives or functional agents must remain within permitted migration limits. Stable melt temperature control, resin homogeneity, and careful material selection are essential to maintaining compliance and long-term stability.
Effective extrusion-coated packaging depends on controlling adhesion, substrate stability, surface quality, and regulatory compliance. When these factors are managed together, the resulting structures deliver reliable barrier performance and meet the technical requirements of modern food packaging applications.
Regulatory Frameworks for Extrusion-Coating Technology Across Countries
| Region | Key Laws / Standards | Scope for Extrusion-Coated Paper/Board | Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | • Framework Regulation (EC) 1935/2004 • GMP Regulation (EC) 2023/2006 • Plastics Regulation (EU) 10/2011 | Plastic layers applied by extrusion coating must comply with positive lists, overall migration limits, and specific migration limits. Paper and board follow national rules. | Verify all coating components are authorized under 10/2011. Conduct migration tests. Check member-state rules for paper and board. |
| United States (USA) | • Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) • Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (21 CFR) Parts 174–178 on indirect food additives • Relevant sections for coatings and paper: 21 CFR 175 (adhesives and coatings) | Extrusion-coated layers used on paper or board are typically regulated as components of food contact materials under 21 CFR. PE must comply with the specific polymer regulations, while coatings on paperboard for aqueous and fatty foods often reference 21 CFR 176.170 and 176.180. | Confirm that each resin, additive, and coating component is cleared under an appropriate 21 CFR section or via a Food Contact Notification. Check intended use conditions match the authorization.Some items limited to ≤0.102 mm for certain high-temperature uses |
| China | • GB 4806.1 General Safety Standard • GB 4806.7 Plastic materials • GB 4806.8 Paper and paperboard • GB 4806.10 Coatings | Extrusion-coated structures often fall under multiple GB standards. Plastic layers follow GB 4806.7, substrates follow GB 4806.8, coatings follow GB 4806.10. | Ensure resins and additives are on the GB positive lists. Perform overall and specific migration tests. Prepare documentation for inspection. |
| Canada | • Food and Drugs Act、 • Health Canada’s Food Contact Materials Guidance • Letter of No Objection (LONO) process for new materials | Extrusion-coated polymers used in food packaging must meet Health Canada safety criteria. Unlisted substances may require a LONO submission. | Confirm coating components meet established food contact policies. Provide migration data if requesting a LONO. Align intended use conditions with Health Canada requirements. |
Sustainability and Biodegradable Lamination Materials
Sustainability in extrusion-coated food packaging is increasingly shaped by the use of PLA and PBAT. Key points include:
- Process Expertise Is Essential
Achieving stable performance with PLA and PBAT requires precise extrusion-coating control. Choosing a manufacturer experienced in processing these materials ensures reliable barrier quality and consistent sustainability benefits. - Core Role of Bio-Based Polymers
PLA and PBAT are now central to sustainable packaging strategies. Their renewable or biodegradable nature aligns with regulatory expectations and consumer demand for lower-impact materials. - Compostable High-Performance Structures
When applied through extrusion coating, PLA and PBAT convert paperboard into compostable structures that maintain moisture and grease resistance. This makes them suitable for salad bowls, bakery formats, and takeaway packaging where compostable waste systems already exist. - Reduction of Fossil-Based Plastics
PLA and PBAT can replace PE in many applications without sacrificing barrier performance. This substitution helps reduce fossil resource consumption and lowers the overall environmental footprint of coated packaging. - Improved End-of-Life Handling
Thin PLA or PBAT coatings are easier to manage in compostable waste streams, and their controlled coating weights lessen environmental burden compared with thicker traditional plastic layers.
All in all, PLA and PBAT provide sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic coatings. Their performance and compostability make them well-suited for modern food packaging needs.
Future Trends in Functional Coating for Food Packaging

Several forward-looking trends are shaping how the industry will adopt and refine Extrusion Coating in the coming decade. The push toward mono-material structures is accelerating, with brands seeking simplified recycling pathways that align with national packaging regulations. Polyolefin-based laminates and all-paper solutions are expected to grow, supported by extrusion-coated barrier and sealing layers.
Bio-based and compostable coatings will likely expand as new resin blends improve heat resistance, flexibility, and barrier performance. As demand for environmentally responsible packaging increases, compostable extrusion-coated structures will serve a wider range of applications beyond food service and fresh produce.
Advances in active and antimicrobial technologies are expected to integrate more seamlessly into extrusion-coated layers. Enhanced oxygen and moisture management, controlled antimicrobial release, and improved regulatory clarity may allow these functionalities to be applied in a broader spectrum of food categories.
Digitalization and process optimization will influence manufacturing efficiency. Improved monitoring tools can stabilize coating thickness, reduce defects, and minimize waste, helping producers balance sustainability, cost performance, and high technical quality in every Functional Coating for Food Packaging produced.
Conclusion
Functional Coating for Food Packaging plays a central role in enhancing the safety, durability, and performance of modern food containers. Among the various technologies used to create these protective layers, extrusion coating serves as one of the most reliable and effective methods. By precisely applying polymers such as PE, PLA, and PBAT onto paper, board, or film, extrusion-coated structures gain essential properties including moisture resistance, grease protection, mechanical stability, and heat sealability, features required across a wide range of food packaging applications. Additional antimicrobial and active coatings further expand functional performance by improving shelf life and product safety.
As sustainability becomes a fundamental requirement rather than an optional advantage, extrusion-coated systems must incorporate renewable materials, optimized coating thicknesses, and thoughtful end-of-life pathways. At the same time, industry expectations for print quality, regulatory compliance, and long-term durability continue to rise. With its unique combination of adaptability, precision, and material compatibility, extrusion coating will remain a foundation for the next generation of innovative, practical, and environmentally responsible food packaging solutions.
FAQs:
1. What is Functional Coating for Food Packaging?
Functional coating for food packaging is a performance layer applied to paper, board, or film to provide moisture resistance, grease control, heat sealability, and stronger structural integrity for safe food contact.
2. How does Extrusion Coating work in food packaging?
Extrusion coating applies molten polymer onto a substrate, forming a continuous protective layer that improves moisture resistance, durability, temperature tolerance, and overall packaging performance.
3. What materials are commonly used in extrusion-coated food packaging?
Common materials include PE for hot and cold applications, PLA for compostable solutions, and PBAT for flexible biodegradable packaging with moisture and grease resistance.
4. Why is functional coating important for food packaging?
Functional coatings prevent leaks, protect against grease, extend food freshness, improve safety, and maintain package strength during filling, storage, and transportation.
5. Are extrusion-coated materials environmentally friendly?
Yes. When using sustainable polymers like PLA or PBAT, extrusion-coated packaging can be compostable or lower in fossil-based plastic, supporting eco-friendly packaging goals.







