After the introduction of UV printing, businesses gained access to faster production, richer color output, and the ability to print directly on wood, metal, glass, acrylic, and even three-dimensional objects. The instant curing process reduced smudging, minimized waste, and made high-quality customization much easier.
Thanks to its adaptability, UV printing serves businesses of all sizes from startups customizing small product runs to large manufacturers producing branded packaging at scale. It performs well on rigid substrates like acrylic and metal, as well as flexible materials like leather or coated paper. Whether for food-safe containers, tech accessories, cosmetics packaging, or event merchandise, this printing method offers durable results with professional-grade detail.
Imagine a local brand preparing for a limited-time product launch. Instead of ordering bulk packaging and risking waste, they use UV printing to create a small batch of compostable boxes featuring full color logos, allergen info, and production codes all printed directly onto the packaging without waiting hours for drying. This means quicker turnaround, less inventory waste, and a faster route to market.
This article is your bridge to fully understanding how UV printing works, why it is transforming modern manufacturing, and how you can use it to improve product quality, expand material options, and streamline production.
Understanding what is uv printing

At its core, UV printing is a digital printing technique that utilizes ultraviolet light to cure specially designed inks during the printing process. The term “UV” refers to the ultraviolet curing system that sets the ink instantly after it’s been applied to the surface. When someone asks, what is UV printing, the simplest answer is that it’s a high-speed, high-precision printing technology that produces crisp, vibrant images on almost any material.
The process begins with the printer applying liquid ink to the substrate. Immediately afterward, a UV light source follows the ink application, curing it on contact. This curing process transforms the ink from a liquid to a solid state within seconds. Unlike traditional inks that absorb into the material, UV inks sit on the surface. This results in more vivid colors, sharper details, and greater durability.
UV printing is not limited to flat surfaces. With advancements like UV flatbed printers, it’s possible to print directly onto irregular or three-dimensional objects. From printing on glass panels and metal sheets to phone cases and wood boards, the versatility is remarkable. The controlled curing process means less ink bleed, reduced waste, and a more eco-conscious production cycle.
How Does UV Printing Work?
UV printing may sound complex at first, but the actual mechanism is a smart combination of precise ink control and rapid curing. The core idea is simple: ink is applied to the surface and then immediately hardened by ultraviolet light. This eliminates the need for heat or air drying and opens the door to printing on materials that would normally reject traditional inks. The entire process relies on three critical components working in perfect sync, the print head, the UV light source, and the ink itself.
Piezoelectric Print Head
At the heart of every UV printer is a piezoelectric print head. This little piece of hardware uses a special crystal that flexes slightly when electricity is applied. That tiny movement forces out extremely fine droplets of ink with pinpoint accuracy. It is not like old-school thermal printing that uses heat to move ink. This system relies on precision pressure instead, which makes it more stable and compatible with a wider variety of inks.
The advantage of the piezoelectric printhead lies in its powerful control. The printer can adjust the droplet size in real time, achieving smooth gradients, sharp edges, and highly detailed images, even on rough or uneven surfaces.
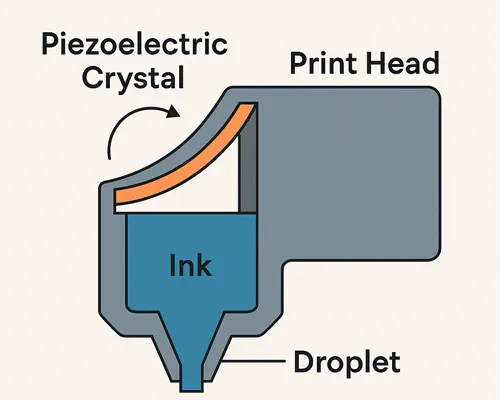
UV Lamp
Once the ink contacts the surface, there’s no need to wait for it to dry. A powerful ultraviolet lamp located next to the printhead instantly cures it. These lamps emit ultraviolet light of a specific wavelength, triggering a photochemical reaction in the ink. In other words, the ultraviolet light instantly cures the ink, firmly fixing it to the surface and preventing it from smudging or being absorbed by the material.
Modern ultraviolet printers typically use LED lamps instead of traditional mercury lamps. LED technology generates less heat and consumes less energy, making it safer and more environmentally friendly.

UV Ink
Unlike traditional inks that dry through evaporation or absorption, UV inks remain liquid until exposed to ultraviolet light. Once exposed to UV light, they cure instantly. This gives them two major advantages: they do not penetrate the material and form a strong, scratch-resistant protective layer on the surface.
UV inks are available in various formulations to meet different printing needs. Regardless of type, these inks typically have a high pigment concentration, resulting in signature vibrant colors and high contrast in printed images. Some UV inks even include a white or transparent layer to enhance depth, gloss, or texture.

Types of UV Printing
There are several forms of UV printing, each tailored for specific types of materials, formats, and use cases. Each type has unique benefits, and the choice depends on the business needs, types of materials involved, and production volume.Here’s a closer look at the primary types:
1. UV Flatbed Printing
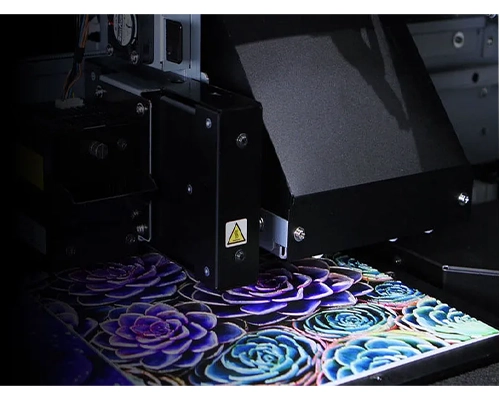

UV flatbed printing uses a stationary bed where the material is laid flat, and a printer head moves over it. This method is ideal for rigid or odd-shaped substrates such as wood, acrylic, glass, metal, and even ceramic tiles. Flatbed printers allow printing on thicker items that cannot pass through traditional printers, offering exceptional control, uniformity, and stability for high-precision graphics and textured effects.
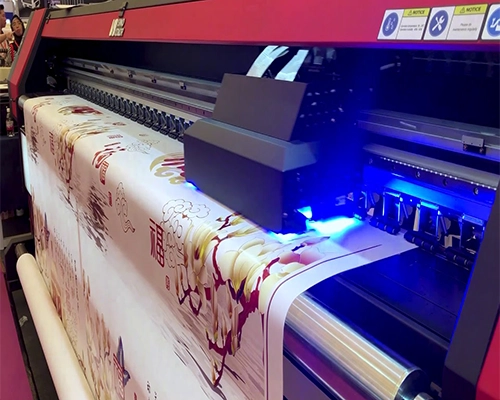
2. UV Roll-to-Roll Printing
UV flatbed printing uses a stationary bed where the material is laid flat, and a printer head moves over it. This method is ideal for rigid or odd-shaped substrates such as wood, acrylic, glass, metal, and even ceramic tiles. Flatbed printers allow printing on thicker items that cannot pass through traditional printers, offering exceptional control, uniformity, and stability for high-precision graphics and textured effects.

3. UV Hybrid Printing
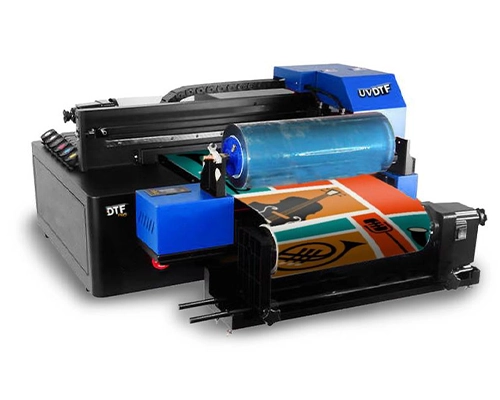

Hybrid UV printing, a combination of flatbed and roll-to-roll systems, offer flexibility to switch between rigid and flexible substrates. This is suitable for businesses requiring a wide range of print jobs without investing in two separate machines. Hybrid setups support varied production needs, allowing quick changeovers, reduced downtime, and greater cost efficiency for companies managing diverse materials and print sizes.
4. Rotary UV Printing
Rrotary UV printing rotates the object while printing, allowing for a full wrap-around image. It is commonly used for customizing bottles, tumblers, jars, candles, and other round containers. The ability to print around the entire object makes this type especially useful for branding in the beverage, cosmetics, and giftware industries.

5. UV DTF Printing
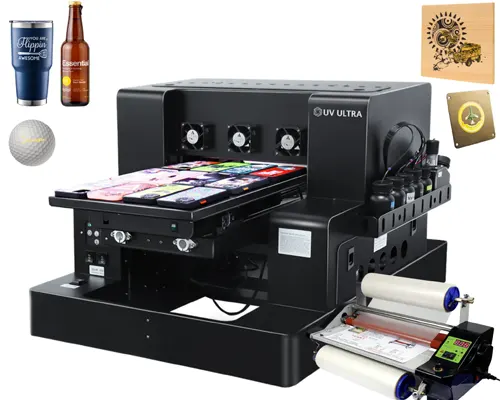

UV DTF printing is a relatively new method that prints the design onto a special film using UV ink. After curing, the film is transferred onto the target surface using adhesive. This technique allows high-quality prints on irregular, curved, or hard-to-reach surfaces without needing to load the actual object into the printer. It’s ideal for items like helmets, curved electronics, or textured gift items where traditional direct printing is tricky.
UV Printing Inks and Materials
One of the reasons UV printing is so versatile is its compatibility with an impressive range of inks and substrates. Understanding the relationship between UV inks and materials is essential for optimizing both print quality and durability.
- Conventional UV Inks
Cure quickly under UV light. Ideal for both rigid and flexible substrates with strong adhesion, vibrant colors, and resistance to scratches and chemicals. - LED UV Inks
Cured using LED lights, these inks reduce heat exposure — great for delicate materials. They’re also energy-efficient and extend lamp lifespan. - Flexible UV Inks
Designed for flexible materials like vinyl and film. These inks can stretch or bend without cracking, making them ideal for packaging films or wraps.



What Materials Can UV Print On:
- Acrylic
Acrylic sheets are one of the most UV-friendly materials. They offer a smooth surface that allows ink to cure evenly and sharply, ideal for signage and displays. - Glass
UV printing on glass works well for high-end branding or decorative applications. White ink improves vibrancy, and the results are clean and long-lasting. - Metal
Metals like aluminum or stainless steel are great for durable signage and product tags. UV ink adheres well and resists wear in harsh environments. - Wood
Wood offers a natural surface for custom prints. Smooth finishes work best, and UV ink can highlight the grain while adding vivid detail for packaging or décor. - Kraft Paper
Commonly used for bakery bags, sandwich wraps, and takeaway boxes. UV printing creates a rustic, eco-friendly aesthetic with clear brand visibility. - Food-grade White Cardboard
Popular in burger boxes, cake trays, and lunch containers. This smooth surface supports full-color UV prints with crisp logos and product info. - Sugarcane Bagasse Paper
A compostable material used for plates, bowls, and lids. UV printing adheres well with flexible ink, maintaining surface integrity and eco appeal. - PLA
A biodegradable plastic used in cold cups and lids. UV printing enables safe, heat-free branding for single-use compostable food packaging.
UV Printing Advantages
UV printing is not just a newer technology. It is a smarter choice for businesses and brands looking for speed, quality, and flexibility. Below are the key advantages that make UV printing stand out in modern manufacturing and packaging workflows.
Durability
One of the most notable strengths of UV printing is the durability of the final output. Since the ink is instantly cured by ultraviolet light, it forms a solid layer that adheres tightly to the surface. This creates a finish that is highly resistant to scratching, moisture, chemicals, and fading. It is particularly beneficial for printed items that are handled frequently or exposed to harsh environments such as food containers, signage, or outdoor product packaging. The print does not peel, smudge, or wear down easily which helps maintain a professional appearance over time.
Versatility
UV printing can be used on an incredibly wide range of materials. From glass, metal, plastic, and acrylic to wood, paperboard, leather, and even ceramics, this printing method works well across both smooth and textured surfaces. It also supports flat, curved, and irregular shapes which makes it suitable for everything from promotional merchandise to industrial parts. Whether printing on takeaway packaging, drinkware, tech accessories, or signage, UV technology adapts with minimal setup.
Vivid Colors
Because UV ink sits on top of the material instead of being absorbed, colors appear more saturated and true to design. The result is vibrant, high contrast prints with excellent visual clarity and sharpness. Whether you are printing branding elements, logos, or photo quality images, UV printing delivers crisp lines and bright color tones that stand out. This is especially valuable in retail packaging and branded items where eye catching visuals make a measurable difference.
Precision
UV printers, especially those equipped with piezoelectric print heads, offer excellent control over ink placement. They can print with extremely fine resolution, handling small text, intricate patterns, and gradient effects with ease. This precision makes UV printing ideal for detailed product labels, serial numbers, QR codes, and any application where clean, readable output matters. Even on textured surfaces like wood grain or leather, the ink lands exactly where it should.
Cost Efficiency for Low Quantities
Unlike traditional printing methods that require plates or long setup processes, UV printing is digital. That means it is perfect for short run jobs, custom orders, or variable data printing with minimal setup cost. Businesses can test new designs, run limited promotions, or fulfill small batch orders without wasting materials or incurring extra tooling fees. This is a big win for startups, small brands, or seasonal campaigns that value flexibility and budget control.
Eco-Friendly Printing Solutions
Modern UV inks are formulated with lower levels of volatile organic compounds and the instant curing process eliminates the need for heat, solvents, or excessive drying equipment. This reduces overall energy consumption and environmental impact. Additionally, UV printing generates less waste due to precise ink application and fewer spoiled prints. For companies focused on sustainability, especially in the food packaging sector, UV printing offers a cleaner and greener solution without compromising on quality or performance.
UV Printing Disadvantages
While UV printing brings significant benefits in speed, quality, and versatility, it is not without its limitations. Like any technology, it comes with trade-offs that should be considered before deciding whether it fits your specific production goals. Below are the main disadvantages to be aware of.
Size Constraints
Most UV printers are limited by the physical size of their print bed or the diameter range of their rotary attachments. This means you may not be able to print on oversized items or very small cylindrical objects without specialized equipment. While flatbed UV printers can handle thick materials, the overall dimensions must still fit within the machine’s capacity. For large format projects such as full wall signage or industrial parts, multiple passes or sectioned printing may be necessary, which increases time and complexity.
Initial Cost
Investing in UV printing equipment often requires a higher upfront cost compared to traditional printing solutions. A basic UV flatbed printer can be a significant expense, and more advanced hybrid or rotary-enabled machines come at an even higher price. On top of that, businesses need to consider the cost of UV-compatible inks, regular maintenance, and operator training. For small companies or startups, this cost barrier can be a major consideration. However, over time, the ability to take on more versatile and profitable jobs may offset the initial investment.
Finish Variability
Although UV printing performs well across many surfaces, the finish of the final print can vary depending on the material, ink type, and curing conditions. On some surfaces, the cured ink may appear too glossy or too matte, and slight texture differences can affect how colors look or feel. In some cases, flexible materials may lead to cracking if rigid inks are used, especially on curved or bendable products. Achieving consistent results across different product types often requires calibration, testing, and sometimes additional pre-treatment steps.
Common Applications of UV Printing

The ability of UV printing to deliver quick, clean, and high-quality results across different surfaces has made it a go-to solution for many industries. Below are eight real-world applications:
- Commercial Signage
Used for billboards, shop signs, and backlit displays. UV printing provides bright, durable colors that hold up in both indoor and outdoor environments. - Takeaway Boxes
Ideal for printing branding, ingredient info, and QR codes directly onto paper or compostable food containers. The print remains sharp through handling and delivery. - Bakery Boxes
Used on cake boxes, pastry trays, and dessert packaging. UV ink adheres cleanly to coated cardboard, offering a premium, smudge-free finish for artisanal and retail use. - Juice and Dairy Bottles
UV printing is applied to PET or HDPE bottles using shrink sleeves or labels, ensuring clear graphics and moisture resistance in refrigerated conditions. - Confectionery Wrappers
Chocolate bars and candy boxes often feature UV-printed seasonal designs. Ideal for short runs and festive packaging with vibrant, high-resolution artwork. - Industrial Components
This ink is used for printing barcodes, serial numbers, and labels on tools, panels, or parts. Examples include large welding machines and PCB board screen printing. The ink is heat-resistant, chemically resistant, and abrasion-resistant, providing durable and reliable performance. - Interior Decoration
Allows high-definition imagery on wood, tiles, glass, or acrylic. Common in wall art, cabinetry, and decorative surfaces for both home and commercial spaces. - Electronics and Gadgets
UV printing enables custom branding on phones, power banks, headphones, and more. The low-heat process protects sensitive components while delivering a clean finish. - Metal Tin Box Packaging
Suitable for high-end gift tins, tea or coffee tins, candy tins, and lip balm tins. UV printing adheres firmly to coated metal surfaces, providing scratch-resistant, high-gloss, or matte finishes. Even with frequent handling, the colors remain vibrant and new, making it ideal for limited editions, seasonal items, or collectible packaging.
Glass and glazed ceramics: They might peel or wrinkle. It’s better to use a pre-coating liquid to help the ink stick.
Metal: It usually prints fine, but if the item gets wet or faces big temperature changes, pre-coating is a good idea.
Acrylic: Works well for everyday use. But if the surface gets scratched a lot, using pre-coating can help protect the print.
Advantages of UV Inks in Food Packaging
UV inks are increasingly used in the food packaging industry, not just for their print quality, but also for their compliance, versatility, and efficiency. Below are the core benefits that make UV inks a smart choice for modern food brands.
Fully Compliant With Food Safety
Food packaging must meet strict health and safety standards, and UV inks are designed with this in mind. Many UV ink formulations used in food applications comply with international regulations such as FDA, EU 1935/2004, and Swiss Ordinance guidelines. When used correctly with functional barrier layers or indirect contact zones, they help ensure safe usage without chemical migration into food. This makes UV printing a reliable choice for brands that prioritize consumer safety without compromising on aesthetics.
Unrivalled Versatility
UV inks can print on almost any packaging substrate, including plastic, coated paper, cardboard, foil, and biodegradable materials. This allows food manufacturers to maintain a consistent, high-quality print across different product lines and packaging formats. Whether you are labeling compostable containers, frozen food trays, or beverage sleeves, UV inks adapt easily. Their instant curing process works well even on temperature-sensitive or non-absorbent surfaces.
An Effective Way To Cut Costs
UV printing eliminates the need for printing plates, drying time, and setup waste, which significantly reduces costs for small and medium production runs. This is especially valuable in food packaging where brands often run seasonal designs, regional variations, or test launches. Being able to quickly switch designs without extra tooling allows for more agile marketing strategies. UV inks also reduce spoilage during production thanks to their instant-drying nature, leading to fewer errors and less material waste.
Reliability
Once cured, UV inks form a strong, durable layer that resists moisture, handling, temperature fluctuations, and scuffing. This is crucial in food supply chains, where packaging must remain intact from factory to shelf. UV prints hold their color and integrity even under refrigeration, transportation stress, or high-speed filling lines. With consistent performance and low failure rates, UV ink provides the reliability food producers need for daily operations and mass distributio
UV Printing vs. Flexographic Printing: Key Differences
| Feature | UV Printing | Flexographic Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Drying Process | Ink cures instantly using ultraviolet light, eliminating smudging and delays | Ink dries through evaporation or heat; slower and prone to smudging |
| Material Versatility | Supports a wide range including plastic, glass, metal, wood, and acrylic | Best suited for flexible packaging materials like film, foil, and cardboard |
| Setup Time and Cost | Minimal setup, ideal for short runs and on-demand jobs | Higher setup time and cost due to plate creation; efficient for long runs |
| Image Durability | Excellent resistance to water, UV exposure, scratches, and chemicals | Good durability but often requires coatings for added protection |
| Print Quality | High-resolution, vibrant, and detailed prints | Moderate resolution; suitable for simple to medium complexity designs |
| Production Speed | Fast with immediate curing and less downtime | Very fast for long continuous jobs once setup is complete |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOCs, minimal waste, especially with LED UV technology | Depends on ink type; water-based inks reduce VOCs, but solvent inks are common |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for short to medium runs and customization | More economical for large-scale, repeatable print runs |
Future of UV Printing
As industries demand greener, faster, and more flexible printing solutions, the evolution of UV printing continues to accelerate.
Technological Innovations in UV Printing
Advancements in printhead design, LED curing systems, and ink formulation are increasing speed and precision. Modern printers offer finer resolution, improved grayscale control, and better color consistency across various substrates. Automation features like AI-powered print management and predictive maintenance reduce downtime and boost output quality.
Hybrid systems that combine UV printing with digital and traditional technologies are also gaining traction, enabling more complex workflows and finishing capabilities in a single pass.
Sustainable Trends and Eco-Ink Development
Sustainability is no longer optional. The latest UV inks are being formulated with fewer harmful chemicals and better biodegradability. Energy-efficient LED curing replaces mercury lamps, reducing power consumption. Some manufacturers are also exploring bio-based inks and recyclable substrates, pushing the entire supply chain toward circular practices.
Regulatory compliance and environmental certifications are also driving innovation, especially in industries like food, healthcare, and retail, where packaging and labeling must meet strict standards.
Conclusion
UV printing is not just a trend. It’s a transformative technology that answers the demand for precision, speed, and flexibility in today’s competitive print markets. From signage to electronics, from packaging to interior design, it empowers creators and businesses to push boundaries without compromising quality or sustainability.
So if you’re still wondering what is UV printing, it’s the future of high-performance, low-waste, multi-surface printing. As new innovations continue to emerge, UV printing is poised to remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing and design for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does UV printing last?
UV printing is highly durable and can last for years without fading or peeling, even with frequent handling or outdoor exposure.
Does UV printing smell?
Freshly printed UV ink may have a mild odor during curing, but once cured, the finished product is odorless and safe to use.
How does UV light contribute to the printing process?
UV light cures the ink instantly by triggering a chemical reaction, allowing it to harden immediately on the surface with no drying time.
How is the 3D texture created?
3D texture is achieved by layering UV ink multiple times, creating raised areas that give the surface a tactile, dimensional effect.
Is UV printing the same as sublimation?
No. UV printing cures ink on the surface using UV light, while sublimation transfers dye into materials using heat and pressure.
Is UV printing environmentally friendly?
Yes. UV printing uses low-VOC inks, produces less waste, and is more energy-efficient than many traditional printing methods.







