Flexible packaging refers to packaging solutions made from materials that can be easily bent, folded, or reshaped without compromising their structural integrity. These materialsoffer a high degree of adaptability while providing essential protection against moisture, oxygen, and external contaminants. Unlike rigid formats like glass jars or metal cans, flexible packaging is engineered to stretch and conform to a product’s shape, making it ideal for applications where durability, efficiency, and space optimization are critical.
As global markets shift toward more efficient, cost-effective, and eco-conscious packaging formats, flexible packaging has rapidly gained dominance. From resealable pouches of pet food to vacuum-sealed coffee bags, flexible packaging has become a daily part of consumer life. The growth of e-commerce, urban living, and on-the-go consumption habits have all contributed to the widespread adoption of this versatile packaging type. Industries are choosing flexible packaging not just for its function, but for its power to tell brand stories through shape, texture, and visual impact.
This in-depth guide will unpack what is flexible packaging, how it works, what materials make it function so effectively, and why it is now seen as the future of packaging innovation. We’ll explore its benefits, compare it with traditional rigid formats, and uncover the industries that depend on its performance. Most importantly, we’ll address the sustainability question,providing a complete understanding of why flexible packaging matters today and tomorrow.
Overview of Flexible Packaging
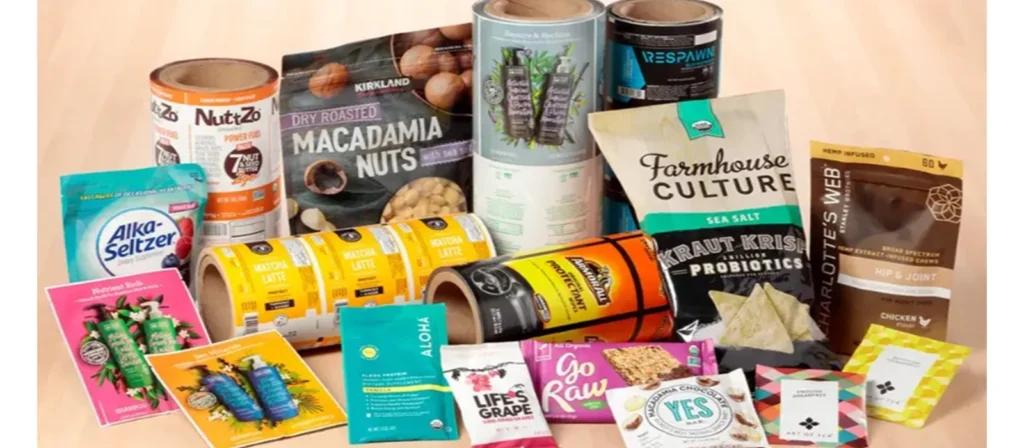

What Is Flexible Packaging is a term that has gained significant attention within the global manufacturing and packaging industries over the last decade. At its core, What Is Flexible Packaging refers to any packaging structure made from flexible or easily yielding materials.materials that can be formed, shaped, folded, or manipulated without losing their integrity. Examples include films, foils, laminates, and specialty papers. Unlike rigid packaging such as glass jars or metal cans, flexible packaging bends, stretches, and conforms while maintaining essential protective properties such as moisture resistance, oxygen barriers, and contamination prevention.
From an engineering standpoint, flexible packaging is built around innovation. It combines the science of materials engineering with user-centric design. Packaging engineers blend polymer films, foil layers, adhesives, and coatings to produce packaging structures that offer strength, barrier protection, and product longevity. Many of these engineered structures incorporate Flexible Packaging materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), and aluminum foil, which together create multilayer films. These multilayer films allow delicate items such as snacks, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices to remain fresh and safe during transport, storage, and consumption.
Businesses continue to adopt flexible packaging because of its exceptional adaptability. It can be shaped into bags, pouches, wrap-around films, liners, rollstock, and even molded forms that resemble rigid packaging. For instance, stand-up pouches can display products on retail shelves in the same way rigid bottles or tubs do,yet require far fewer raw materials and reduce transportation costs significantly.The rising popularity of flexible packaging is also linked to the digital transformation of the packaging industry. Digital printing technology enables short-run, customizable packaging for marketing campaigns, seasonal promotions, or limited edition product launches. This level of customization is far easier and more cost-effective with flexible packaging than with rigid alternatives.
At a fundamental level, flexible packaging embodies efficiency. It uses fewer resources, weighs less, offers excellent protective qualities, and can be engineered to enhance sustainability. While challenges remain,especially around end-of-life recycling,the industry continues to push toward recyclable monomaterials, biodegradable films, and energy-efficient production techniques. Understanding What Is Flexible Packaging means recognizing it as a constantly evolving field, one driven by science, consumer needs, environmental pressures, and global logistics trends.
What are some common materials for flexible packaging?

Flexible packaging depends heavily on high-performance materials that combine durability, safety, and tailored barrier properties. At the heart of these structures are Flexible Packaging materials, each chosen for its unique characteristics. These materials are engineered to protect products from oxygen, moisture, light, chemicals, microorganisms, and physical damage.
1. polyethylene (PE)
PE is valued for its flexibility, clarity, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is commonly used in bags, wraps, and inner liners, while high-density polyethylene (HDPE) appears in applications where slightly more rigidity is needed.
2. Polypropylene (PP)
PP offers excellent clarity, heat resistance, and strength, making it ideal for snack packaging, bakery films, and microwaveable containers. PP films maintain product freshness by preventing vapor transmission while also providing important sealing properties.
3. Polyester (PET)
PET films are commonly laminated with other layers to create a structure that resists stretching, tearing, and temperature fluctuations. This makes them suitable for foods that require extended shelf life, such as coffee, frozen goods, and dehydrated meals.
4. Aluminum foil
Foil provides an impenetrable barrier against light, moisture, and oxygen. Many food and pharmaceutical products rely on foil to maintain sterility and prevent spoilage. Foil-based flexible packaging is a favorite in industries where shelf stability is critical.
5. Paper
Paper, although often overshadowed by films and foils, remains highly relevant. Kraft paper and coated paper can be combined with polymer layers for added strength and protection. Paper-based pouches and bags are used heavily in dry foods, pet foods, and health products because of their natural, sustainable appearance.
6. Laminates
Laminates,multilayer structures composed of two or more materials,are arguably the most important innovation in flexible packaging. Laminates combine the strengths of different components to create packaging that is lightweight yet highly protective. A laminated structure may include PET for strength, aluminum foil for barrier performance, and PE for sealing. This synergy enables packaging that meets very specific requirements for shelf life, structural integrity, and aesthetics.
7. Advanced composite materials
These include bio-based films derived from plant materials such as cellulose or corn starch, as well as compostable films that break down under industrial composting conditions. Innovations in monomaterial films,structures made from one type of polymer instead of multiple,address end-of-life recycling challenges by simplifying the recycling process.
Flexible packaging materials continue to expand as industries push for sustainable, high-performance solutions. Understanding these materials is essential for anyone seeking to fully grasp What Is Flexible Packaging and its role in global commerce.
What are the benefits of flexible packaging?

Flexible formats improve transport efficiency and align with corporate sustainability initiatives seeking greener alternatives.
1. Cost Efficiency
- Flexible packaging uses fewer raw materials compared to rigid containers, significantly lowering both manufacturing and overall operational costs.
- It occupies less storage space and reduces fuel consumption during transportation, saving money across the supply chain.
2. Material Efficiency
- Its lightweight and compact nature enables manufacturers to boost production capacity while generating minimal waste output.
- The streamlined manufacturing process also conserves natural resources and reduces energy consumption in the long term.
3. Superior Barrier Protection
- Engineered film layers and laminates create a high-performance shield against oxygen, UV light, moisture, and odors.
- This reliable protection ensures extended shelf stability and quality preservation for perishable and sensitive products.
4. Enhanced Branding and Shelf Appeal
- With support for vibrant, high-definition graphics and unique shapes, packaging can serve as a powerful marketing tool.
- Flexible materials allow for customization in design, texture, and visual presentation to attract target consumers more effectively.
5. Consumer Convenience
- Resealable zippers, easy-tear notches, and ergonomic spouts cater to on-the-go lifestyles and repeated usage.
- These features enhance user experience by improving accessibility, portability, and product freshness after opening.
6. Production and Logistical Efficiency
- Flexible packaging works seamlessly with modern high-speed machinery, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity.
- Pre-fabricated pouches and wraps simplify assembly lines, minimize downtime, and cut long-term operational costs.
7. Sustainability Advantages
- It contributes to environmental responsibility by requiring less material and generating a smaller carbon footprint.
- Flexible formats improve transport efficiency and align with corporate sustainability initiatives seeking greener alternatives.
What are the types of flexible packaging?
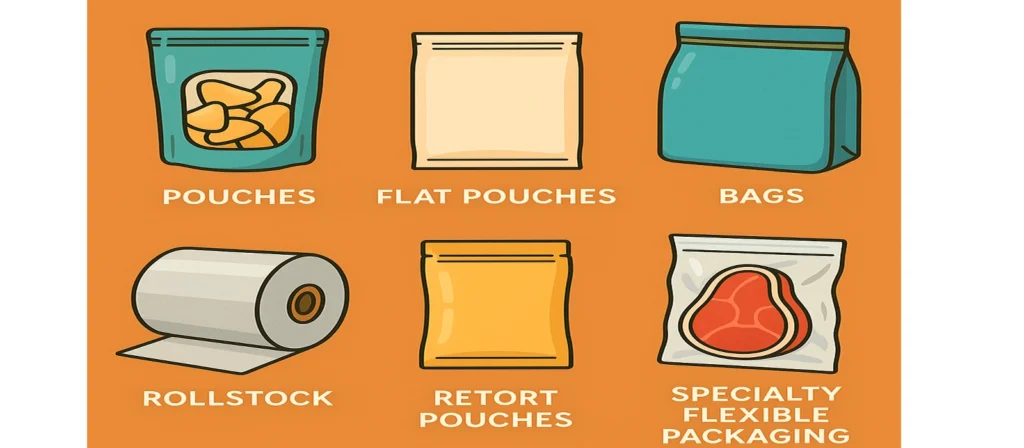
Flexible packaging comes in many forms, each designed to meet specific industry and product needs. Pouches are among the most recognizable and versatile forms. Stand-up pouches, for example, offer excellent shelf presence and are widely used for snacks, beverages, household items, and pet foods. These pouches can be equipped with resealable features, spouts, or transparent windows to enhance functionality and visual appeal.
- Flat pouches and pillow pouches:Flat pouches and pillow pouches provide simple yet effective packaging for items such as spices, powders, medical devices, and single-serve foods. Their streamlined form makes them cost-effective and efficient to produce.
- Bags:Including wicketed bags, gusseted bags, and zip-lock bags, serve a broad range of applications from bakery items to frozen foods. These bags are typically made from Flexible Packaging materials such as LDPE or PP, providing durability and practicality.
- Rollstock: is commonly used in automated packaging systems. Manufacturers use rollstock to create form-fill-seal (FFS) packaging for high-speed production lines. Rollstock films can be customized for printing, laminating, and sealing to match specific product requirements.
- Retort pouches: are another key category, designed to withstand the high temperatures of retort sterilization. These pouches provide shelf-stable packaging for soups, sauces, ready-to-eat meals, and baby food.
- Shrink films and stretch films: are used heavily in logistics and retail. Shrink films conform tightly to products once heat is applied, offering tamper resistance and product security. Stretch films secure pallets and protect goods during transport.
- Specialty flexible packaging: such as vacuum bags, barrier films, and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) solutions play essential roles in preserving freshness and extending shelf life for sensitive food products.
Flexible Packaging vs. Rigid Packaging
| Aspect | Flexible Packaging | Rigid Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material Usage | Uses significantly fewer raw materials due to lightweight and thin-film construction. | Requires more raw materials such as glass, metal, or thick plastic. |
| Weight & Transport | Lightweight, reduces shipping costs and storage needs. | Heavier, increases transportation expenses and storage requirements. |
| Barrier Protection | Offers excellent barrier properties with multilayer films (moisture, oxygen, UV). | Provides strong protection, especially against physical damage. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower material and logistics costs; ideal for cost-sensitive industries. | Higher production and transportation costs due to bulk and material density. |
| Customization | Highly adaptable; supports resealable, spouted, and shaped formats for marketing. | Limited customization; typically fixed shapes and sizes. |
| Sustainability | Lower material use and emissions, but recycling is challenging due to multilayers. | More recyclable (glass, metal), but higher carbon footprint in production and transport. |
| Production Efficiency | Works well with high-speed, automated machinery and reduces labor needs. | Slower production lines and more labor-intensive processes. |
| Shelf Impact | Can be printed with vibrant graphics and innovative formats to boost brand visibility. | Offers good visibility but less dynamic in appearance and design. |
| Use Cases | Best for snacks, pharmaceuticals, liquids, and on-the-go products. | Preferred for beverages, fragile goods, and bulk items requiring rigid protection. |
| Environmental Trends | Moving towards monomaterials and recyclable structures to improve eco-friendliness. | Focus remains on reuse and recycling of existing rigid materials. |
Which industries rely on flexible packaging?
Flexible packaging is used across nearly every major industry. The food and beverage industry represents the largest segment due to the need for freshness, convenience, branding, and cost efficiency. Snacks, frozen foods, tea, coffee, sauces, spices, and beverages are all commonly packaged in flexible formats.
1. Pharmaceutical and medical
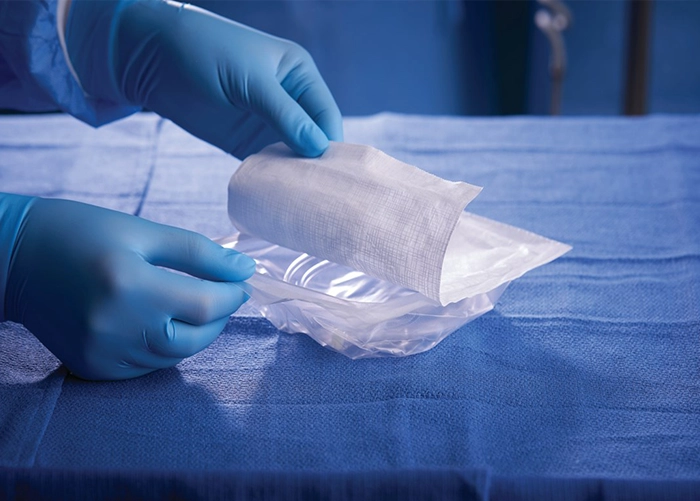
The pharmaceutical and medical industries rely heavily on flexible packaging for sterile barrier systems, medical device packaging, capsule pouches, and protective films. These industries require highly engineered Flexible Packaging materials with strict barrier and safety standards to ensure patient safety and compliance with global regulatory frameworks. Additionally, tamper-evidence and product traceability features are critical in pharmaceutical applications, further reinforcing the need for advanced packaging solutions.
2. Cosmetics and personal care
Cosmetics and personal care brands increasingly rely on flexible packaging for a wide range of products, including creams, lotions, sample sachets, wipes, and various beauty tools. The lightweight, portable, and user-friendly nature of flexible packaging aligns exceptionally well with fast-paced, modern consumer habits and aesthetic preferences, especially in travel-size and single-use products. This packaging also allows brands to experiment with unique shapes, finishes, and high-quality printing for enhanced shelf appeal.

3. Agriculture

In agriculture, flexible packaging plays a critical role in protecting seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and animal feed products from moisture, contamination, and physical damage. The use of heavy-duty films and multi-layer laminated bags ensures long-lasting product stability and safety during handling, transportation, storage, and field application—essential for maintaining agricultural productivity.
4. Chemical and Industrial
Chemical and industrial sectors utilize flexible packaging for items like lubricants, adhesives, powdered substances, and hazardous or corrosive materials. Flexible formats ensure secure, leak-proof containment, controlled dispensing, and safe handling while withstanding rigorous environmental conditions, thereby reducing the risks associated with industrial chemical packaging. In addition, barrier properties and puncture resistance are tailored to meet demanding safety regulations and high-performance usage requirements.

5. Pet food

Pet food companies depend heavily on flexible packaging, especially durable stand-up pouches and multi-wall bags, for preserving freshness, nutritional integrity, and product durability. These packaging formats are not only cost-efficient and resistant to tearing but also provide convenient storage, resealability, and attractive branding that appeals to pet owners in a highly competitive market. Many brands also incorporate clear windows, matte finishes, and eco-friendly materials to meet rising consumer expectations.
This diverse range of applications clearly highlights the universal importance and growing reliance on flexible packaging across a wide spectrum of global industries, from everyday consumer goods to highly specialized sectors.
Does flexible packaging have an environmental impact?

The environmental impact of flexible packaging is a complex topic. On one hand, flexible packaging uses fewer materials and results in lower carbon emissions during transportation. Its lightweight nature reduces resource consumption and energy use throughout the supply chain.However, the challenge lies in end-of-life disposal. Many flexible packaging structures are made from laminated or multilayer materials that are difficult to recycle due to the combination of plastics, foils, and coatings. Traditional recycling systems are not equipped to separate these layers efficiently.
Despite these challenges, sustainability innovations are rapidly advancing. Monomaterial films,made from a single polymer such as all-PE or all-PP,are designed to be more easily recyclable. Compostable films and bio-based materials offer renewable alternatives.Chemical recycling technologies are emerging as well, converting mixed polymer waste back into usable feedstock. These innovations hold potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of flexible packaging.
Brands are increasingly committing to sustainable packaging commitments, pushing suppliers to develop recyclable, biodegradable, and circular packaging solutions.Understanding the sustainability landscape is critical for anyone researching What Is Flexible Packaging today.
What is the future of Flexible Packaging Technologies?

The future of flexible packaging is driven by technological innovation, consumer preferences, and sustainability demands. Smart packaging technologies incorporate sensors, QR codes, freshness indicators, and track-and-trace systems, enhancing transparency and improving supply chain management.
Digital printing allows brands to personalize packaging, reduce waste, and create faster product launches. Variable data printing supports serialization for pharmaceuticals and regulatory compliance.Advances in Flexible Packaging materials are accelerating the development of recyclable monomaterials, compostable films, and improved barrier coatings that eliminate the need for aluminum layers.Automation is transforming packaging production. High-speed form-fill-seal machinery, robotics, and AI-driven quality control are streamlining operations and reducing costs.Sustainable adhesives, water-based inks, and bio-based laminates are reducing reliance on fossil fuels and improving recyclability.
The next decade will likely redefine what flexible packaging can achieve,pushing it toward smarter, greener, more efficient solutions that meet global market demands.
Conclusion
Understanding What Is Flexible Packaging involves exploring its materials, benefits, applications, and technological advancements. Flexible packaging continues to dominate global markets due to its efficiency, sustainability potential, protective capabilities, and adaptability. As industries seek to reduce their environmental footprint while improving product performance, flexible packaging stands at the forefront of innovation. With ongoing advancements in Flexible Packaging materials, sustainability technology, and digital production, the future of this packaging solution is both promising and transformative.
FAQs
1. What Is Flexible Packaging and why is it important?
Flexible packaging refers to any packaging made from flexible materials such as films, foils, or paper. It is important because it reduces material usage, provides excellent barrier protection, and enhances convenience.
2. Are flexible packaging materials recyclable?
Some are, particularly monomaterial films. Multilayer laminates remain more challenging to recycle, but new technologies continue to improve recyclability.
3. Which industries benefit most from flexible packaging?
Food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, agriculture, and industrial sectors rely heavily on flexible packaging for efficiency and product protection.
4. Is flexible packaging more sustainable than rigid packaging?
In many cases, yes. Flexible packaging uses fewer materials and lowers transportation emissions. However, recycling access must continue improving.
5. What materials are used in flexible packaging?
Common materials include PE, PP, PET, aluminum foil, paper, and multilayer laminates.
6. How is flexible packaging evolving?
New innovations include smart packaging, recyclable monomaterials, digital printing, and advanced barrier technologies







