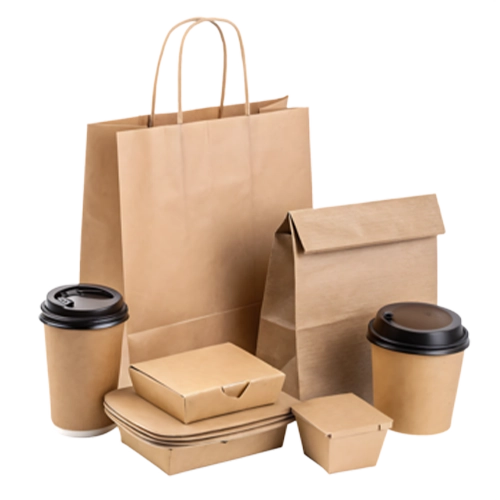
PE coated paper is a paper-based material that has been covered with a thin layer of polyethylene on one or both sides to improve its barrier and mechanical performance. In simple terms, it is still paper at its core, but the surface is sealed with plastic so that it can resist water, oil, and general wear much better than ordinary paper. This combination allows the material to keep the natural look, stiffness, and easy printability of paper while gaining additional protection where direct contact with liquids or grease is expected.
You can easily recognize PE coated paper in everyday items. The smooth inner surface of a disposable cup, the glossy inside of a takeaway box, or the leak-resistant wall of a soup container are typical signs of a PE coating. This guide will walk you through the essentials of PE coated paper so you can make informed decisions in this changing landscape.
Types of PE Coated Paper for Food Packaging
PE coated paper used in food packaging is typically classified based on how many sides of the paper are coated with polyethylene. The two main types are single-sided and double-sided PE coated paper. Each serves different functions depending on the food product, the packaging method, and the required resistance to moisture or grease.
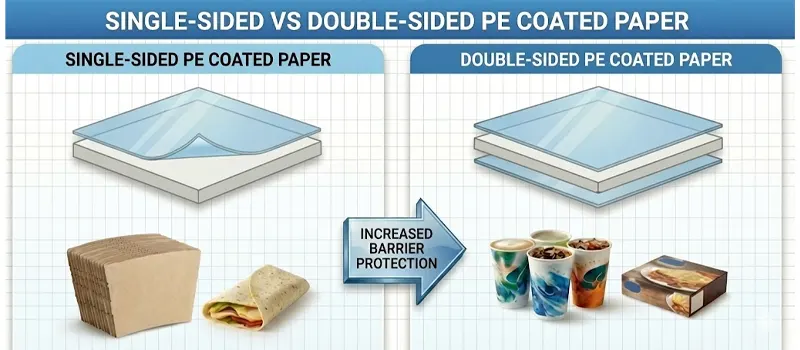
Single-Sided PE Coated Paper
Single-sided PE coated paper has a polyethylene layer applied to only one surface. The coated side provides resistance to water, oil, and steam, while the uncoated side keeps the natural paper texture for easier printing and handling. This structure works well for applications where only the inner side of the packaging needs protection. It is commonly used for food wraps, bakery bags, and paper boxes that hold dry or lightly greasy foods.
Double-Sided PE Coated Paper
Double-sided PE coated paper has polyethylene applied to both surfaces to create stronger barrier performance. With protection on both sides, the material can handle hot, oily, or high moisture foods without softening or losing strength. This type is widely used for coffee cups, soup containers, and ice cream tubs where both the inner and outer surfaces must resist liquid absorption and maintain shape during use.
How is PE Coated Paper Manufactured?
The manufacturing of PE coated paper is a controlled process that combines base paper with melted polyethylene to form a sealed and durable surface. Each step influences the final barrier strength, smoothness, and suitability of the material for food packaging.

1. Base Paper Preparation
The process begins with selecting and preparing the base paper, which can be white bleached paper or kraft paper, depending on the intended application. The paper is unwound from large rolls and inspected to ensure stable strength, smooth fiber structure, and proper moisture content. Choosing the right base paper ensures the polyethylene layer bonds evenly and prevents wrinkling during production.
2. Polyethylene Melting and Extrusion
Polyethylene pellets (usually LDPE or LLDPE) are heated to a molten state using an extruder. Once melted, the plastic is ready to be applied to the paper. The temperature and extrusion speed are precisely controlled to maintain coating consistency.
3. Coating Application
The molten polyethylene is extruded through a flat die onto the moving base paper. The coating can be applied to one side (single-sided) or both sides (double-sided), depending on the requirement. This process is known as extrusion coating, and it creates a direct bond between the plastic and the paper surface.
4. Cooling and Solidification
After the polyethylene is applied, the coated paper passes through a series of chill rollers. These rollers cool the material rapidly, helping the PE layer solidify and bond tightly with the paper. The cooling stage also helps smooth out the surface and prevent warping or uneven coating.
5. Rewinding and Cutting
Once cooled and inspected, the PE coated paper is rewound into large rolls or sheets. It can then be cut to specific sizes based on customer needs. Additional steps, such as printing, laminating, or converting into packaging products, may follow.
What Is the Appearance of PE Coating Paper?
The polyethylene layer creates a smooth, sealed surface that can be either glossy or matte, depending on the treatment process. The coating reduces the natural roughness of the paper fibers and creates a sealed surface that resists moisture and grease. This appearance is stable, clean, and suitable for food packaging that requires both strength and visual consistency.

Glossy Finish Treatment
A glossy finish on PE coated paper is achieved by applying a smooth, high-density polyethylene layer during the extrusion process. The surface appears shiny and reflective due to the way light interacts with the smooth plastic coating. This type of finish enhances the visual appeal of packaging, giving products a clean, modern, and hygienic look.
Glossy PE coated paper is commonly used in applications where presentation matters, such as food service packaging, beverage cups, and premium takeaway containers. The glossy layer also provides excellent protection against moisture, oil, and staining, making it suitable for both hot and cold contents.
In addition to its appearance, the glossy surface offers better print clarity and color vibrancy. This makes it ideal for branded packaging that requires detailed logos, product images, or promotional messages. However, the surface may not be suitable for writing with pens or markers, as ink may smear or fail to adhere properly.
Matte Finish Treatment
Matte PE coated paper is produced by adjusting the surface texture during the coating process or by using a thinner polyethylene layer. The result is a smooth yet non-reflective surface that diffuses light evenly. It offers a more natural and understated appearance compared to the glossy version.
This finish is often chosen for packaging that requires a softer, more premium aesthetic or for functional purposes where glare reduction is important. Matte PE coated paper is also easier to write on with pens or markers, making it practical for labeling and wrapping applications.
Despite its subdued look, matte coating still provides effective resistance to water and grease. It performs well in applications like sandwich wraps, bakery paper, and cartons, where contact with moist or oily items is expected but where high visual shine is not desired.
Key Features of PE Coated Paper
PE coated paper offers a combination of barrier protection, durability, and visual quality that makes it suitable for a wide range of food packaging needs. The polyethylene layer strengthens the surface and allows the material to handle moisture, oil, and various temperatures with greater stability than uncoated paper.
- Water Resistance
The PE layer acts as a moisture barrier, preventing the paper from absorbing liquids. This makes it ideal for cold drink cups, food trays, and wrapping materials exposed to wet conditions. - Oil and Grease Resistance
PE coated paper resists oil penetration, keeping packaging clean and intact when used with greasy or fried foods such as burgers, pastries, and snacks. - Improved Tear Strength
The plastic coating adds tensile strength, reducing the risk of tearing or deformation during handling, folding, or sealing. - Smooth Surface Finish
The coating creates a consistent, sealed surface that can be either glossy or matte. This enhances printability and gives the product a professional appearance. - Heat Sealability
PE coated paper can be sealed using heat, making it suitable for forming containers, pouches, or lids without the need for adhesives. - Customizable Coating
Coating can be applied on one or both sides, with different thickness levels to suit specific packaging needs and barrier requirements. - Compatibility with Printing
The coated surface supports high-quality printing for branding and product information, especially when using flexographic or offset techniques. - Food Contact Safety
When produced under proper standards, PE coated paper is food-safe and compliant with regulations for direct contact with edible items.
Advantages of PE Coated Paper in Packaging
PE Coated Paper combines barrier strength, durability, and practical usability, allowing it to perform reliably in many food service environments. These advantages support both product safety and consumer convenience.

Reliable Food Protection
The polyethylene layer strengthens the barrier against moisture, oil, and external contaminants. This protection helps maintain the freshness and cleanliness of packaged foods and supports longer shelf life in takeaway or delivery settings.
Cost Effective Performance
PE coated paper provides dependable barrier strength at a more economical cost compared with many fully plastic materials. Its stable supply chain and mature manufacturing process also help businesses maintain predictable production budgets.
Improved Customer Experience
The smooth and refined surface makes the packaging comfortable to hold and helps prevent leakage from hot or oily foods. This creates a more pleasant and hygienic experience for customers, especially in busy food service environments.
Supports High Speed Packaging
PE coated paper has consistent heat sealing ability, good dimensional stability, and uniform surface structure. These features allow it to run smoothly on automated packing lines and help manufacturers increase efficiency while reducing material waste.
Wide Range of Applications
The material can be used for hot and cold food containers, sandwich wraps, tray liners, cups, ice cream tubs, and medical pouches. Its versatility makes it valuable across many industries where lightweight and reliable packaging is required.
Customizable for Branding
The coated surface supports high-quality printing and allows businesses to add logos, product details, and marketing messages directly on the packaging. Clear and consistent print results help improve brand recognition.
Available in Eco-Friendly Options
Depending on the base paper and production method, PE coated paper can be produced with recyclable or FSC certified materials. This supports sustainability goals and helps brands align with market expectations for responsible packaging.
Ease of Conversion and Processing
PE coated paper works well with common converting methods such as die cutting, folding, heat sealing, and printing. Manufacturers can form it into various shapes without complex changes to equipment. This allows efficient production of packaging in large volumes and supports consistent quality across batches.
Common Applications of PE Coated Paper
PE coated paper is widely used across the food service and packaging industry because it offers stable barrier protection and reliable strength. Its ability to resist moisture, oil, and heat makes it perform well in environments where uncoated paper would soften or lose shape.

- Disposable Food Containers
Used for cups, bowls, plates, and trays that hold both hot and cold food. The PE coating prevents leakage and maintains the shape of the container during use. - Food Wraps and Liners
Ideal for sandwich wraps, burger paper, and bakery liners, where grease and moisture control are critical. The coated side faces the food to provide protection, while the uncoated side may allow for easy folding or sealing. - Takeaway and Fast Food Packaging
Common in takeaway boxes, snack bags, and pizza liners, offering a clean and reliable barrier that keeps packaging intact and hygienic during transport. - Frozen and Refrigerated Food Packaging
Used in frozen food wraps, meat pads, and dairy cartons. The polyethylene layer prevents the paper from absorbing moisture and maintains product quality in cold storage conditions. - Medical and Sanitary Packaging
Applied in medical pouches, surgical supply wraps, or personal hygiene packaging that requires clean, sealed surfaces and resistance to contamination. - Industrial and Agricultural Uses
Utilized as liners for boxes, sacks, or bags where dust or moisture protection is needed, such as in fertilizer bags, cement sacks, or chemical packaging. - Retail and Consumer Packaging
Includes shopping bags, product wraps, and branded packaging where a smooth surface and strong print quality are desired alongside protection.
Comparison with Other Types of Coated Papers
Different coatings offer different levels of moisture protection, grease resistance, temperature performance, and environmental characteristics. Understanding these differences helps buyers choose the most suitable material for their product requirements and brand goals.

PE Coated Paper vs Wax Coated Paper
Wax-coated paper uses a thin layer of wax to provide water resistance, giving it a soft and slightly oily feel. It works well for short-term wrapping of baked goods or deli items, but loses strength when exposed to heat and does not offer reliable protection for liquids. PE-coated paper provides a stronger and more durable barrier that remains stable under hot or cold conditions. It keeps its shape better, supports higher quality printing, and is suitable for containers that must resist steam, oil, and moisture for longer periods.
PE Coated Paper vs PET Coated Paper
PET-coated paper uses a polyester film to create a very strong barrier that resists moisture, oxygen, and grease. It offers excellent durability and heat resistance, which makes it suitable for oven-ready or high-temperature applications. However, PET coating increases production cost and can make the material stiffer and less flexible for common food service containers. PE coated paper delivers reliable performance for most cups, bowls, and boxes while remaining more cost-efficient and easier to process on standard packaging lines.
PE Coated Paper vs PLA Coated Paper
PLA coated paper uses a plant-based coating made from polylactic acid and is valued for its compostable properties in industrial composting facilities. It performs well with cold foods and some warm items, but is more sensitive to heat compared with PE coated paper. For applications such as hot drinks, soup containers, or fried foods, PE-coated paper offers more stable sealing and stronger shape retention. PLA-coated paper is chosen for specific sustainability goals, while PE coated paper remains the more versatile and widely used option across food service packaging.
How to Choose the Right PE Coated Paper Packaging?
Choosing the right PE coated paper packaging depends on understanding the food product, the service environment, and the required performance during filling, transport, and consumption. By reviewing barrier needs, heat tolerance, printing goals, and production conditions, buyers can select packaging that performs reliably and delivers a positive customer experience.

Regulatory and Food Contact Compliance
Food packaging must meet the regulatory requirements of the target market. Verification includes not only coating safety but also migration limits, hygiene management, and documentation. Suppliers should provide compliance certificates and traceability records. Ensuring regulatory alignment reduces risks during audits, cross-border shipping, and retail distribution.
Consider the Type of Food
The moisture level, oil content, and serving temperature of the food influence the required coating structure. Hot drinks, soups, and oily foods perform better in double-sided coated paper, while dry or lightly moist items often work well with single-sided coated material.
Serving Conditions: Dine-in vs. Takeaway
Dine-in service needs packaging that is easy to hold and stable for short-term use. The main focus is comfort and clean handling. Takeaway service requires packaging with stronger barrier performance and better structural strength because it must stay intact during transport and handling. Considering these two conditions helps determine which paper structure is more suitable.
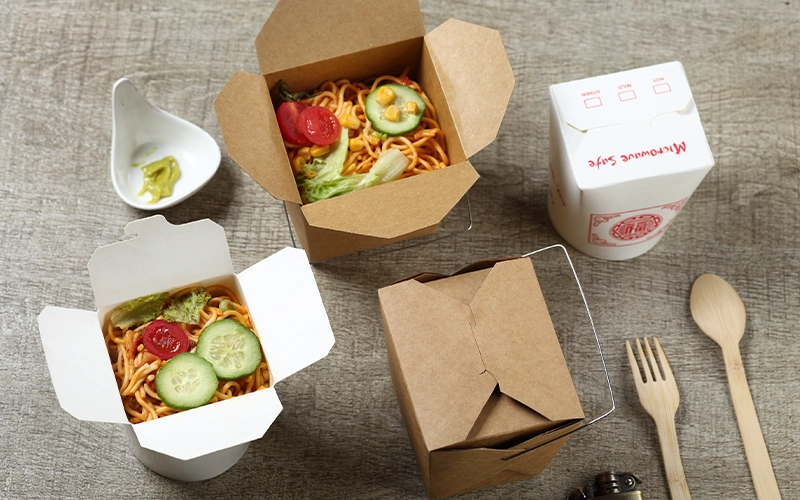

PE Coated Paper Packaging
Durable takeaway boxes made with PE coated paper, suitable for both hot and cold foods. Perfect for restaurants, cafes, and food delivery brands that require reliable grease resistance and a clean professional presentation.
Browse MoreBase Paper Selection
Cups, large bowls, and trays require paperboard with higher stiffness to maintain structure. Lighter wraps or liners can use lower weight base paper. Selecting the proper base paper ensures the final packaging remains stable during use and transport.
Evaluate Barrier Strength Requirements
Different applications require different barrier levels. For strong moisture protection, thicker PE coating provides more stability. For items with heavy grease, a higher-quality coating on the contact side helps prevent stains and keeps the outer surface clean.
Surface Finish
Glossy PE coating provides a high-shine appearance and supports sharp, vibrant printing, making it suitable for consumer-facing packaging. It also improves perceived hygiene and brand visibility. Matte coating offers a more natural, soft look with lower reflectivity, often preferred for eco-conscious brands or applications where the surface needs to be written on.
Cost and Production Efficiency
Evaluate the balance between material performance and overall cost. Single-sided coatings are generally more economical, while double-sided versions offer better protection. Consider roll width, coating weight, and printability in relation to your production setup to avoid waste and improve throughput.
Future Trends in PE Coated Paper Industry
The PE coated paper industry is moving toward greater sustainability, stronger technical performance, and broader global adoption. These trends are shaped by market demand, evolving regulations, and continuous improvements in coating technologies.

Sustainability and Environmental Innovation
More attention is being placed on coating structures that reduce environmental impact. Manufacturers are developing biodegradable and recyclable coating systems that can serve as alternatives to traditional PE layers. These new solutions aim to maintain barrier strength while meeting stricter environmental regulations and supporting corporate sustainability goals. At the same time, the industry is actively exploring technologies that support circular economy principles by improving material recovery and reducing overall plastic use.
Enhanced Barrier Performance and Specialized Applications
Coating technologies continue to advance, leading to paper grades with stronger moisture and oil resistance. These improvements help expand the use of PE coated paper in food and beverage packaging that requires higher durability. Demand is also rising in sectors such as e-commerce and retail, where packaging must stay strong during long transport and repeated handling.
Strong Growth Driven by Food Delivery
The rapid expansion of takeaway and delivery services increases demand for packaging that resists heat, steam, and transport stress. PE coated paper will continue to be adapted for higher stiffness, stronger sealing, and improved performance in both hot and cold service conditions. This trend is expected to remain strong across Asia, North America, and Europe.
FAQs
Can PE coated paper be recycled?
PE coated paper can be recycled in facilities that are equipped to separate the plastic layer from the paper fibers. Recycling availability varies by region, but more mills are investing in fiber recovery systems to support paper-based packaging.
Is PE coated paper biodegradable?
PE coated paper is not fully biodegradable because the polyethylene layer does not break down naturally. The paper fiber can degrade, but the PE layer remains. It is not suitable for composting, although some regions can recycle it through fiber recovery systems.
Is PE coated paper food-safe?
Yes, when manufactured under proper standards, PE coated paper is safe for direct food contact. It is commonly used for cups, wraps, and containers in the food industry and complies with food safety regulations such as FDA, EU 1935/2004, or GB 4806.
What makes PE coated paper different from regular paper?
PE coated paper includes a thin layer of polyethylene that blocks moisture and oil from penetrating the paper fibres. This barrier keeps the material stiff, clean, and functional when in contact with liquids or grease, unlike regular paper.
What are the disadvantages of PE coated paper?
PE coated paper is difficult to biodegrade because the plastic layer does not break down naturally. It requires specialized recycling facilities to separate the coating from the paper. It can also be less suitable for brands that prioritize plastic-free or fully compostable packaging.
Conclusion
PE coated paper remains one of the most reliable and widely used materials in food packaging because it offers strong moisture resistance, dependable grease protection, and stable performance across hot and cold applications. By combining the natural strength of paper with the protective qualities of polyethylene, it provides a balance of durability, functionality, and print quality that supports many food service and consumer packaging needs.
As sustainability expectations continue to grow, the industry is developing lighter coatings, improved recyclability options, and more efficient production methods. These developments ensure that PE coated paper will remain an important solution while evolving to meet future regulatory and market requirements. Through innovation, PE coated paper can continue to deliver safe, attractive, and reliable packaging for a wide range of food products.







